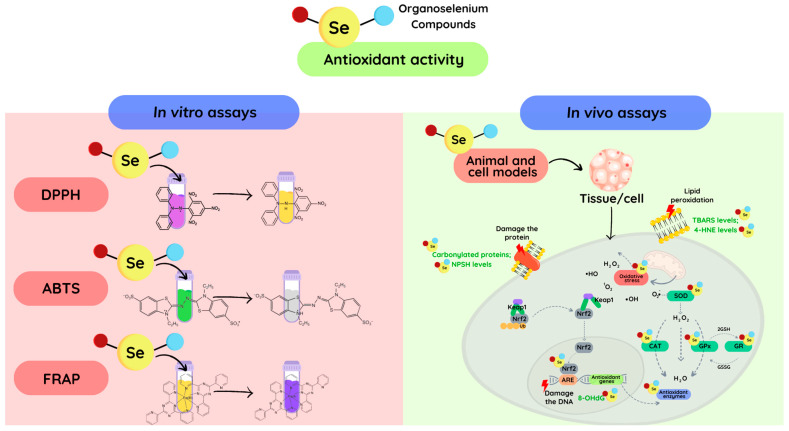
Figure 1.
The routes of the mainly antioxidant assays for exploring the antioxidant properties of novel organoselenium compounds. The antioxidant properties can be studied in a cell through the reduction of the oxidative damage caused to DNA, proteins, and cell membranes, or by mimicking antioxidant enzymes (SOD, CAT, GPx, etc.). Additionally, the redox activity can be observed in vitro through the reduction of oxidant concentrations or synthetic radicals, such as DPPH and ABTS. Finally, oxidants can be directly measured using specific techniques, such as electron paramagnetic (spin) resonance and fluorescent probes. In the DPPH assay, after the reduction of the DPPH radical the color changes from purple to pale yellow. In the ABTS assay, upon reduction of the ABTS radical, the green color discoloration occurs. In the FRAP test, the reduction of Fe3+ yields a violet-blue color.