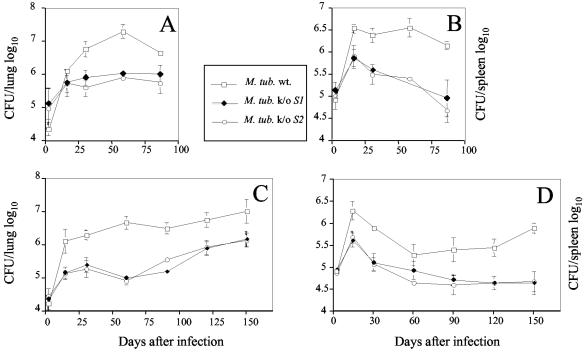
FIG. 3.
Growth of pstS1 (M. tub S1−) and pstS2 (M. tub S2−) knockout mutant and wild-type (M. tub wt.) M. tuberculosis strains in lungs (A and C) and spleens (B and D) of infected mice. The bacteria were grown as a surface pellicle on synthetic Sauton medium for 14 days at 37°C and then harvested and homogenized by ball mill as previously described (16). The M. tuberculosis H37Rv wild-type and pstS1 and pstS2 knockout mutant strains were used to infect BALB/c (A and B) and C57BL/6 (C and D) mice intravenously with 2 × 105 CFU from the different M. tuberculosis H37Rv strains. At the indicated time points, the spleen and lungs from individual mice were homogenized in phosphate-buffered saline, and serial threefold dilutions were plated in duplicate onto Middlebrook 7H11 oleic acid-albumin-dextrose-catalase medium and incubated at 37°C for 3 to 4 weeks. The bacteria were then counted visually, and the numbers of CFU per organ were determined. The results represent the mean log10 values ± standard deviations of at least four mice per group. The mice (3 to 4 months old at the time of infection) were bred in the animal facilities of the Pasteur Institute of Brussels from breeding pairs obtained from Bantin and Kingman (Grimston, United Kingdom).