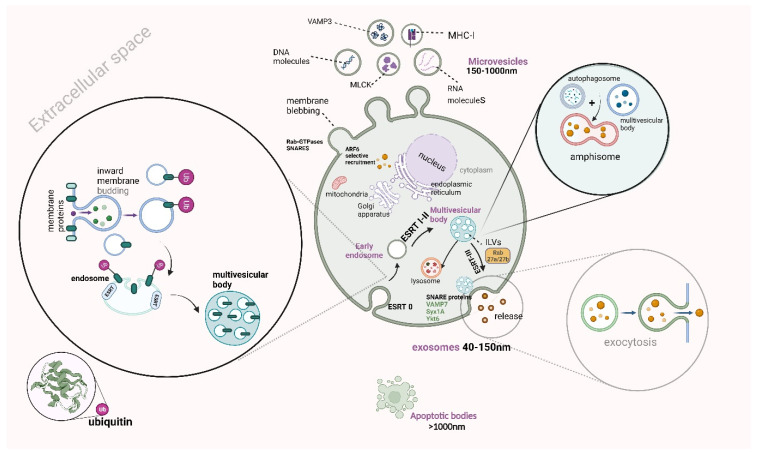
Figure 1.
A schematic presentation of different routes of EV biogenesis. Exosomes are produced via the inward budding of the plasma membrane, resulting in the internalization of proteins under the effect of the endoplasmic network, which leads to the formation. The vesicles are split from the cell membrane, forming the early endosomes, which are further matured into late endosomes. Later, intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) are formed, which give rise to multivesicular bodies (MVBs) that fuse with the plasma membrane, releasing the exosome into extracellular space. However, MVBs can fuse with autophagosomes, resulting in amphisomes, which are either transferred to lysosomes for degradation or fused with plasma membrane for exosome exocytosis. Microvesicles are produced via the outward blebbing of the plasma membrane, while apoptotic bodies result from the cell apoptosis process, leading to apoptotic cell body generation, which gives rise to apoptotic bodies after their fragmentation. This figure was created with “BioRender.com”, accessed on 19 October 2023 (Agreement number UL25ZPCH0P).