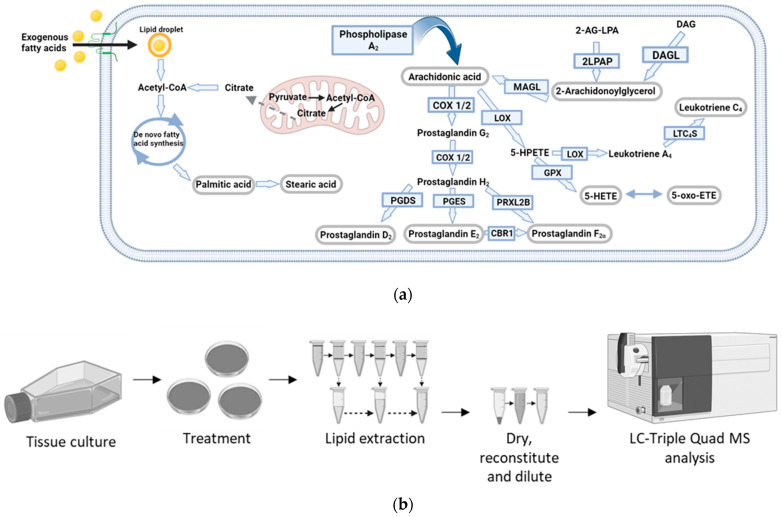
Figure 1.
Eicosanoid pathway and methodology workflow. (a) Metabolic pathways of selected bioactive lipids. Converting enzymes are in boxes and the lipids in this study are circled in grey. De novo lipogenesis leading to fatty acid synthesis, which results in the elongation of fatty acids, produces Palmitic acid and Stearic acid. Exogenous fatty acid uptake is carried out via transmembrane transporters. (b) Optimised experimental workflow for the analysis of eicosanoids and fatty acids was conducted using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography-dMRM-MS (UPLC-dMRM-MS). Cells were cultured in IMDM media containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) and grown until 60–70% confluent. Cells were then treated with 1000 U/mL of IFNα-2b for 36 h, reaching ~80% confluence. The surrounding media (the cell supernatant) was collected from the plates and cells were lysed. Lipid extraction from cells and cell supernatants was performed with Methanol/Methyl tert-butyl ether/chloroform (MeOH/MTBE/CHCl3) and acetonitrile (ACN), respectively. Lipid extracts were subsequently dried and reconstituted in 50% (v/v) MeOH (in H2O) prior to LC-MS analysis.