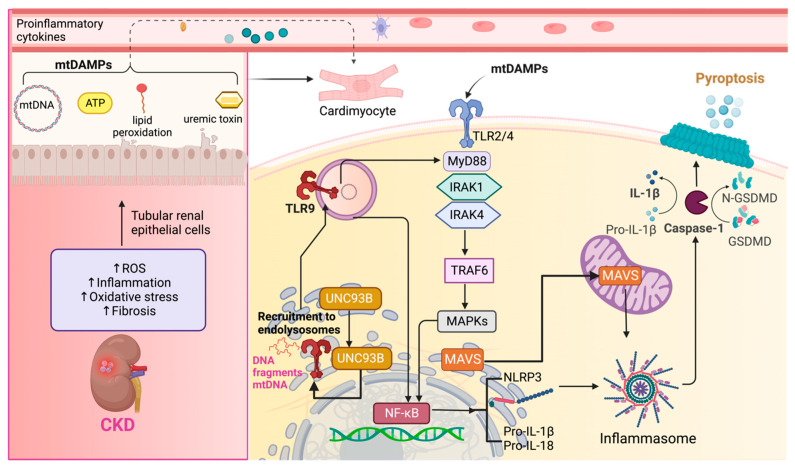
Figure 3.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in cardiorenal syndrome type 4 (CRS type 4). In chronic kidney disease (CKD), several factors contribute to the initiation of inflammation, oxidative stress, and fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. These cellular insults result in the release of Damage-associated Molecular Patterns (DAMPs), including mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid (mtDNA), ATP, peroxidized lipids, and uremic toxins, which play a pivotal role in mediating inflammatory responses in cardiomyocytes and the recruitment of inflammatory cells. mtDNA, extracellular ATP, peroxidized lipids, and uremic toxins can activate membrane-bound Toll-like receptors, specifically TLR2 and TLR4. The activation of these receptors is mediated by the adaptor molecule myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88). Once TLR2 and TLR4 are engaged, they initiate the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) pathway. Activated MAPKs ultimately lead to the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor involved in the regulation of inflammatory genes. NF-κB promotes the assembly of the NOD-like receptor (NLR) family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome. Within this complex, pro-interleukin-1 beta (pro-IL-1β) and pro-interleukin-18 (pro-IL-18) are processed to form the mature and active IL-1β and IL-18. TLR9 might be activated by internal, external, or mtDNA, which induces the recruitment of TLR9 by UNC93B protein from the endoplasmic reticulum to endolysosomes. It leads to the activation of MAPKs mediated by MyD88 by following the same steps of TLR2 and TLR4. The activation of NLRP3 results in a cascade of events, ultimately leading to pyroptosis. Pyroptosis is mediated by gasdermin D (GSDMD), which forms pores in the cell membrane, causing cell lysis and the release of pro-inflammatory intracellular contents. The mitochondrial antiviral proteins (MAVS) also activate NLRP3, leading to pyroptosis induction. IL-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAK), IRAK1 and IRAK4, TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF-6). Figure created by using Biorender.com.