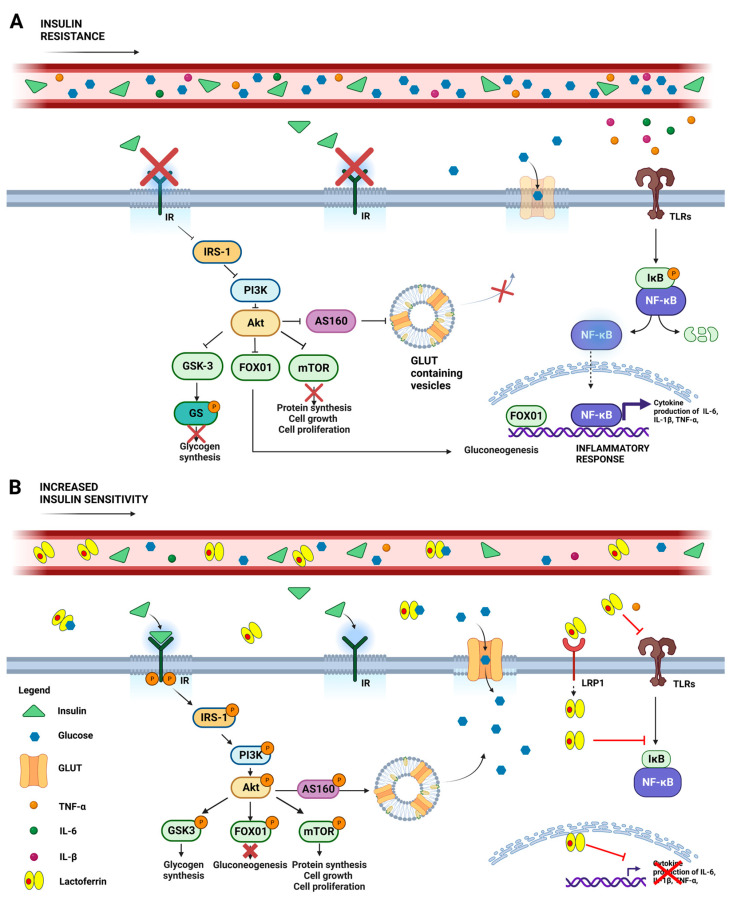
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of systemic glycemic disorders in the absence (A) or presence (B) of lactoferrin. (A) Insulin resistance is a clinical condition where insulin’s ability to promote glucose absorption and utilization is impaired, resulting in elevated blood glucose levels. This condition hampers IR autophosphorylation, which impairs the IRS-1/PI3-kinase/AKT pathway and results in aberrant downstream signals, including GSK3 activation and the consequent inhibition of glycogen synthesis via the phosphorylation of GS; the reduction of mTOR-mediated protein synthesis, cell growth and proliferation; as well as FOX01nuclear translocation, which promotes gluconeogenesis and the inflammatory response. Stimulation of TLRs by TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β exacerbates insulin resistance through the inflammatory IKβ/NF-κB pathway, increasing cytokine expression. (B) Lactoferrin treatment counteracts these detrimental effects by boosting insulin binding to IR, thereby activating the IRS-1/PI3-kinase/Akt pathway. Akt activation results in AS160 phosphorylation, prompting GLUT to relocate from intracellular vesicles to the cell membrane, thus improving glucose uptake. Simultaneously, Akt-mediated FOX01 phosphorylation inactivates its nuclear translocation, while GSK3 and mTOR phosphorylation promote glycogen and protein synthesis, respectively. In addition, the protective effect of Lf could be explored by its ability to bind glucose and by virtue of its anti-inflammatory activity, thus counteracting TLR-mediated detrimental signaling. Abbreviations: insulin receptor (IR); insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1); phosphatidyl inositol 3-kinase (PI3-Kinase); Akt, also known as protein kinase B; GSK3 (glycogen synthase kinase-3); GS (glycogen synthase); FOX01 (forkhead-box protein 01); Toll-like receptors (TLRs); tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6); interleukin-1β (IL-1β); nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB); inhibitor of NF-κB (IKβ); glucose transporter (GLUT). Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 15 June 2023).