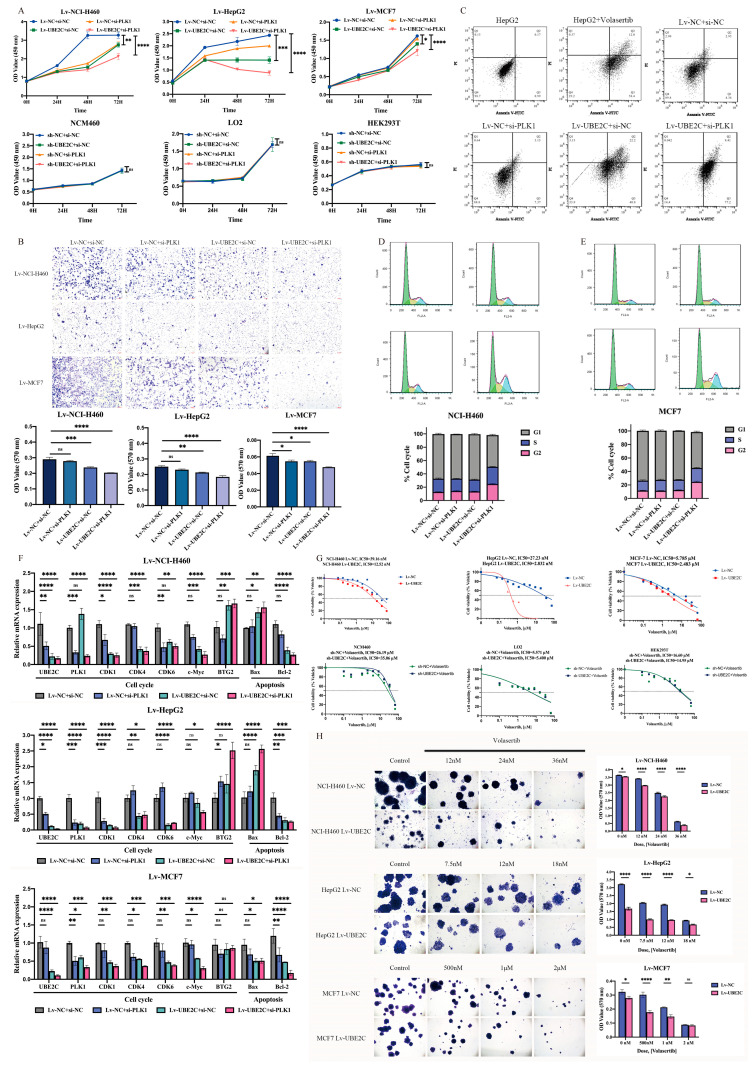
Figure 3.
Combined inhibition of UBE2C and PLK1 could more significantly reduce the malignant phenotype of pan-cancer cells. (A) Co-interference with UBE2C and PLK1 significantly inhibited cancer cell (top panel) proliferation but not that of normal cells (bottom panel) at different time points. (B) Co-interference with UBE2C and PLK1 significantly inhibited cancer cell migration. The microscopic images were captured at 10× magnification. The bar graph on the right represents the detection of the OD value at 570 nm of crystal violet staining of the treatment group and the control group. The value represents mean ± SEM. (C) Co-interference with UBE2C and PLK1 significantly promoted cancer cell apoptosis. The number of apoptosis cells detected by flow cytometry. Graphical representation of % cell death (Q2+Q3) from three different experiments on HepG2 cells. (D,E) Co-interference effects of UBE2C and PLK1 on cell cycle of (D) NCI-H460 and (E) MCF7. FACS analyses were performed using si-NC or si-PLK1-transfected Lv-NCI-H460 or Lv-MCF7 cells for 24 h. Cell number (%) in each cell cycle phase is indicated in the graph. Grey color in bar graph indicates G1 phase, and blue and pink colors indicate S and G2 phases, respectively. (F) The expression levels of cell-cycle- and apoptosis-related genes were detected via qRT-PCR after co-interference with UBE2C and PLK1 in Lv-NCI-H460, Lv-HepG2, and Lv-MCF7 cells (from top to bottom). (G) PLK1 inhibitor volasertib inhibited the viability of UBE2C stable knockdown cells (top panel), but normal cells were not sensitive (bottom panel). (H) Combined treatment of interfering UBE2C with volasertib remarkably repressed cancer cells’ colony-forming capacity. The microscopic images were captured at 4× magnification. The bar graph on the right represents the detection of the OD value at 570 nm of crystal violet staining of the treatment group and the control group. All the values represent mean ± SEM. ns—No significance, *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001; ****: p < 0.0001 (a two-way ANOVA was used, except for (B), in which an ordinary one-way ANOVA was used).