Figure 2.
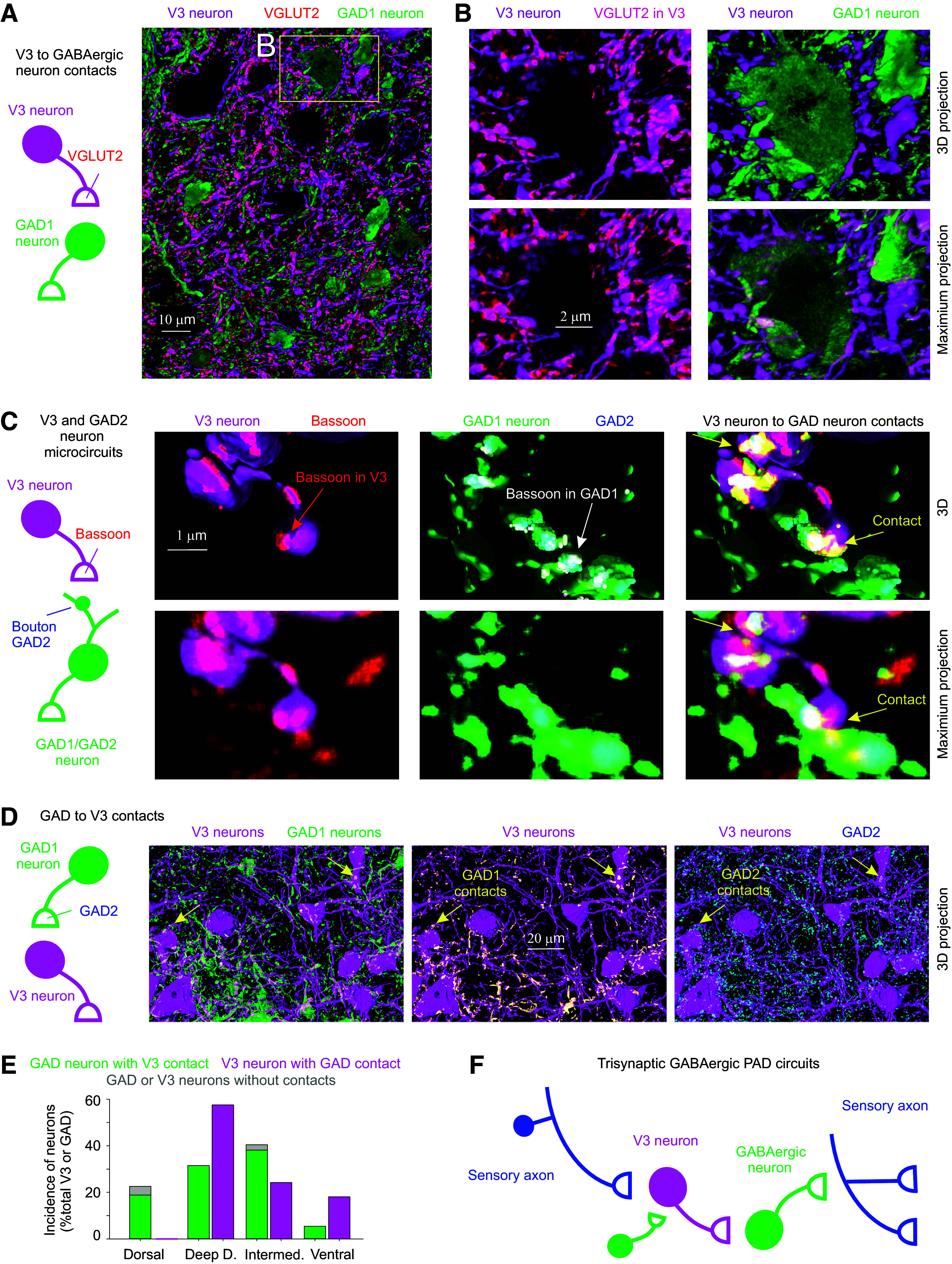
Connections between V3 neurons and GABAergic neurons that produce PAD. A and B: V3 neurons (tdTom) contact onto GABAergic neurons, where presynaptic V3 neuron contacts are VGLUT2+(red), the vesicular transporter expressed in these glutamatergic V3 neurons. Spinal cord from mouse expressing Sim1//tdTom (magenta, V3) and GAD1-GFP (green, GABAergic neurons). Images shown both as 3-D reconstructions (3-D) and raw images (maximum projection of image stack). C: close up of V3 neuron contacts (Sim1//tdTom) onto GABAergic neuron (GAD1-GFP), with V3 presynaptic terminal labeled with bassoon and GABAergic neuron labeled with GAD2, the latter to show that it is a GAD2+ neuron. Bassoon is also expressed in the GABAergic neuron boutons near the GAD2 clusters and the V3 contacts. D: GABAergic (GAD1-GFP) neurons also innervate V3 neurons, with GAD2+ presynaptic contacts. E: neuron soma distributions for V3 (n = 52) and GABAergic (n = 146) neurons in the deep dorsal, intermediate (VII), central canal (cc, X) and ventral laminae, and incidence of contacts (VGLUT2+ or bassoon+) on soma from either V3 neurons or GABAergic neurons, from 3 mice. F: schematic summarizing trisynaptic circuit mediating PAD with the addition of a contact from GABAergic neurons onto V3 neurons that inhibits the circuit. PAD, primary afferent depolarization.
