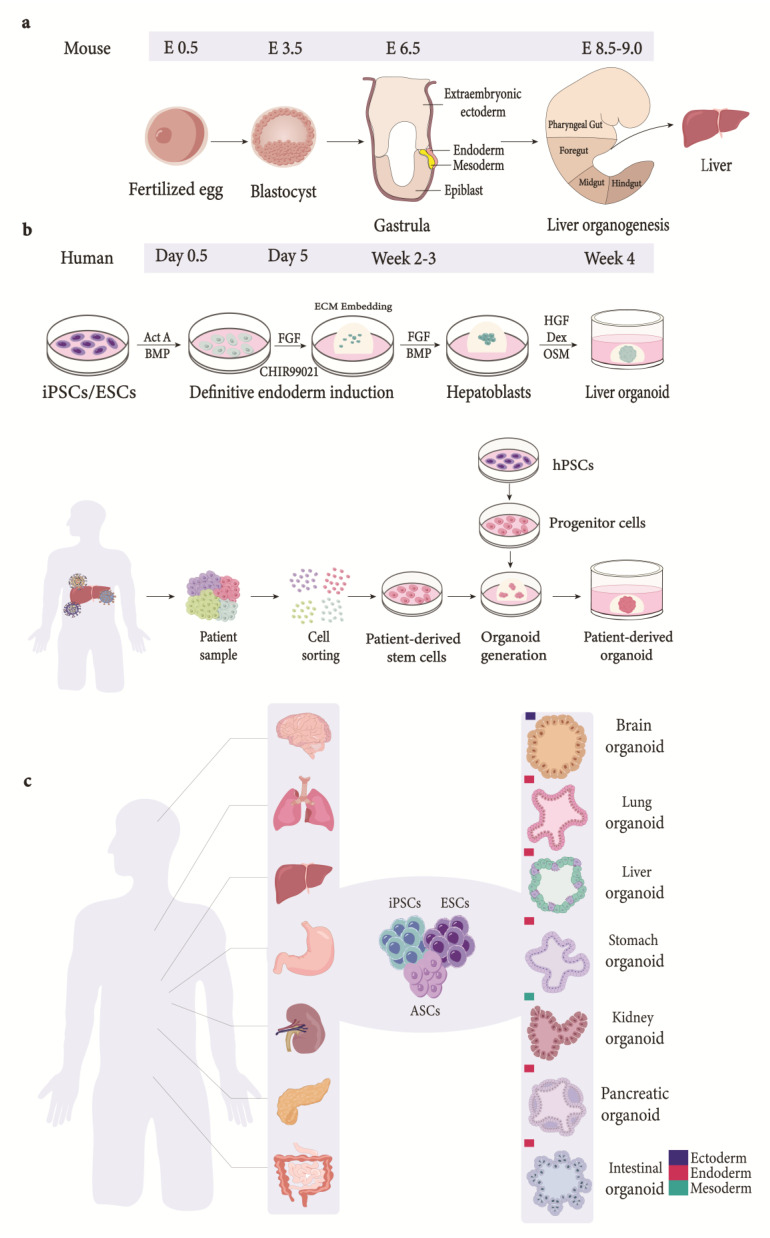
Figure 2.
Organogenesis and generation of liver organoids from various sources. (a) Schematic depiction of stages involved in organogenesis. Embryo formation is followed by blastocyst stage. The blastocyst consists of an outer layer of trophectodermal cells and ICM. The ICM, consisting of embryonic stem cells, further specializes into either epiblast lineage or primitive endoderm lineage during the late stages of its formation. Blastocyst is followed by gastrulation, where morphological rearrangements transform epiblast into the three germ layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm [16,17]. The endoderm becomes patterned into anterior foregut (AF), posterior foregut (PF), midgut (M), and hindgut (H). As illustrated above, the liver is derived from PF domain of the endoderm. (b) Organoids derived from pluripotent stem cells follow a stage-wise differentiation process that recapitulates signaling pathways observed during development. The differentiation process starts by directing iPSCs/ESCs towards endodermal fate when exposed to Act A and Wnt. The cells are embedded in ECM and differentiated into hepatoblasts-like cells (progenitor cells) using FGF and BMP. Hepatoblast-like cells differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells via exposure to OSM [18,19]. Moreover, ductal organoids can be generated by modulating FGF, EGF, and Act A signaling [16]. Hepatoblasts embedded in ECM give rise to hepatic organoids. Several tissue sources have been used to generate patient-derived organoids using a number of different techniques for tissue processing. The variation in techniques used has led to non-standardized patient-derived organoid culture techniques [20]. In general, tissue-derived stem cells are dissociated into single cells and embedded in extracellular matrix to generate organoids [21,22]. (c) Generation of organoids. Organoids generated for various organs derived from the three germ layers. ICM, inner cell mass; Act A, Activin A; BMP, bone morphogenetic protein; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; ECM, extracellular matrix; HGF, hepatocyte growth factor; OSM, Oncostatin M; Dex, dexamethasone; iPSCs, induced pluripotent stem cells; ESCs, embryonic stem cells; hPSCs, human pluripotent stem cells; ASCs, adult stem cells.