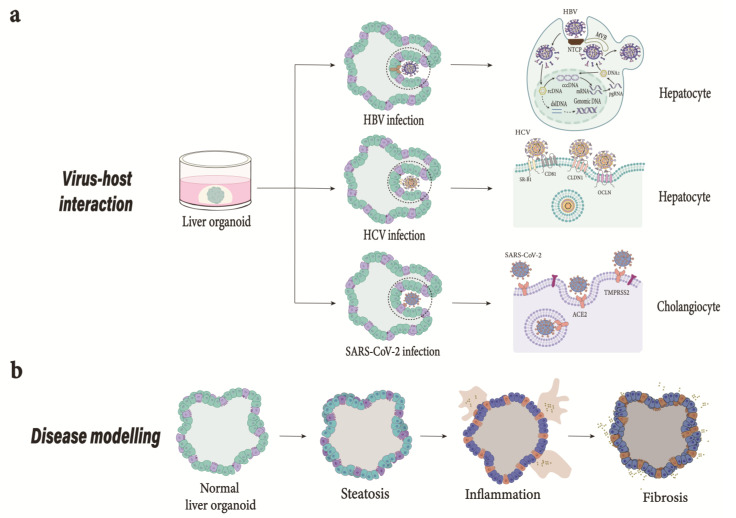
Figure 3.
Application of liver organoid models. (a) Virus host interaction. HBV; Modeling HBV infection and drug screening. The model developed can successfully recapitulate HBV infection [21]. Depiction of HBV life cycle from attachment to secretion of viral particles. HBV enters hepatocyte via a mechanism involving NTCP receptor. Once internalized, the HBV’s rcDNA genome liberated into the nucleus is converted into cccDNA, which serves as a template for transcription. The dslDNA produced can either integrate into cellular genome or convert into cccDNA. The viral mRNA transported to cytoplasm is translated into viral proteins. The pgRNA and viral polymerase are encapsulated and reverse transcribed into progeny rcDNA within the nucleocapsid. HCV; The importance of new models to study HCV is crucial due to limited animal models [52]. Organoids derived from adult stem cells and hPSCs can be used to further our understanding of HCV infection and develop antiviral drugs. HCV interaction with cell surface receptors initiates viral entry. HEV; Generation of liver-derived organoids support HEV infection and life cycle and could help develop new therapies. SARS-CoV-2; The interaction of spike protein with ACE2 receptor in the presence of TMPRSS2 facilitates the entry of SARS-CoV-2 into the host cell. COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 could mediate cell damage, dysregulate RAAS leading to decreased cleavage of angiotensin I and angiotensin II, thromboinflammation, and endothelial cell damage, and inhibit interferon signaling, i.e., depletion of T lymphocytes and production of cytokines such as IL-6 and TNFα [76]. (b) Modeling steatohepatitis in vitro. The failure of animal models in identifying translatable therapies highlights the need for improved models. Generation of organoids from patient-derived hPSCs consisting of multiple hepatic cell types successfully emulates liver-in-a-dish and can be utilized to study liver inflammation and fibrosis and identify effective drug treatments [18]. NTCP, Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide; rcDNA, relaxed circular DNA; cccDNA, closed circular DNA; dslDNA, double-stranded linear DNA; pgRNA, pregenomic RNA; ACE2, Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; TMPRSS2, transmembrane protease, serine 2; RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; IL-6, interleukin 6; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha.