Figure 1. Associations between social support and epigenetic aging in the Health and Retirement Study.
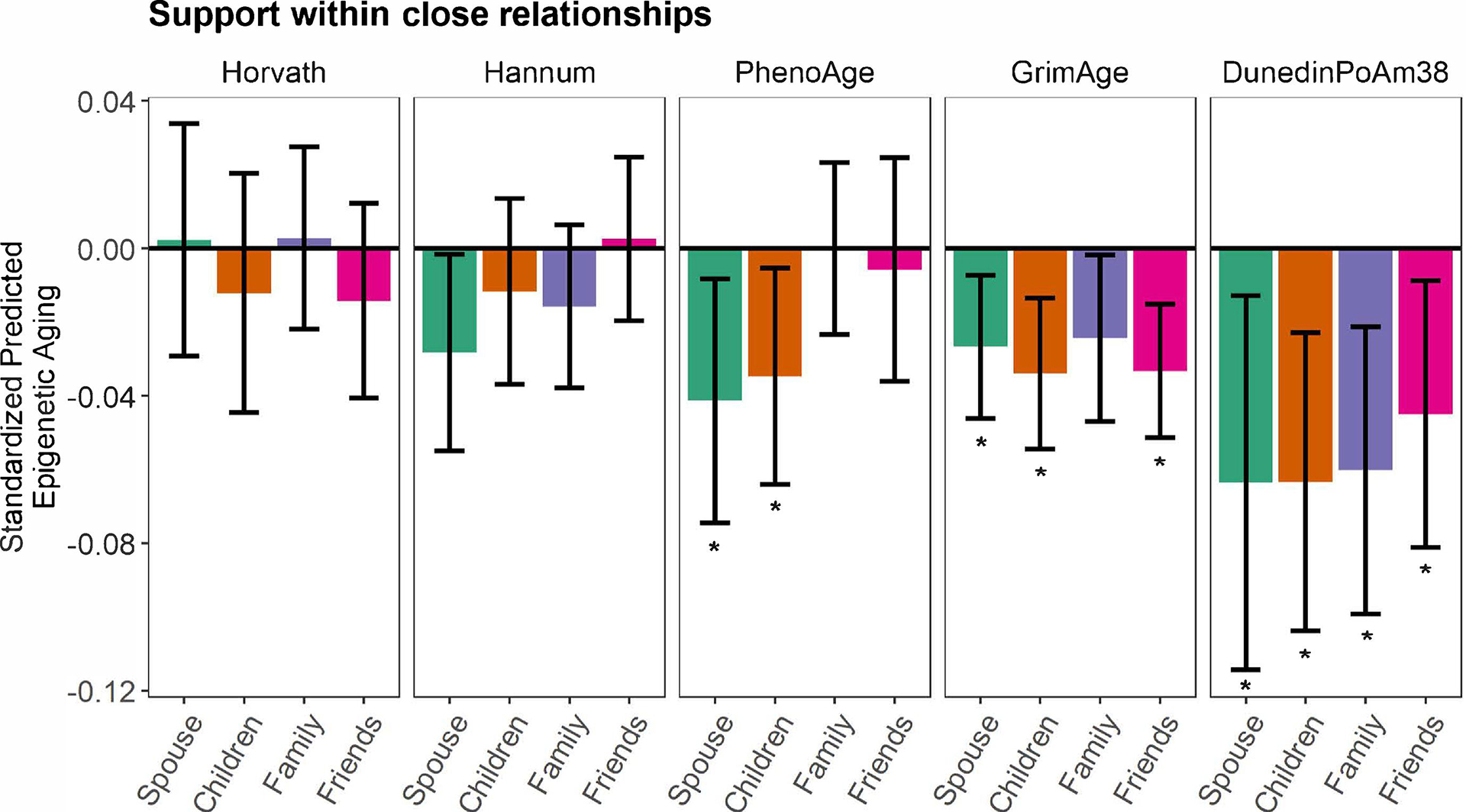
Generalized linear models (GLMs) with standardized coefficients (relationship and epigenetic aging variables were z-scored) showing associations between perceived support from one’s spouse, child, other family members, and friends and epigenetic aging. Models adjusted for chronological age, biological sex, and self-identified race/ethnicity. Error bars represent 95% confidence intervals for each point estimate. Asterisks denote associations that remained statistically significant following false discovery rate correction for multiple testing. Associations between support from friends and family members and GrimAge and DunedinPoAm38, respectively, remained statistically significant in secondary models that further adjusted for educational attainment and lifestyle factors.
