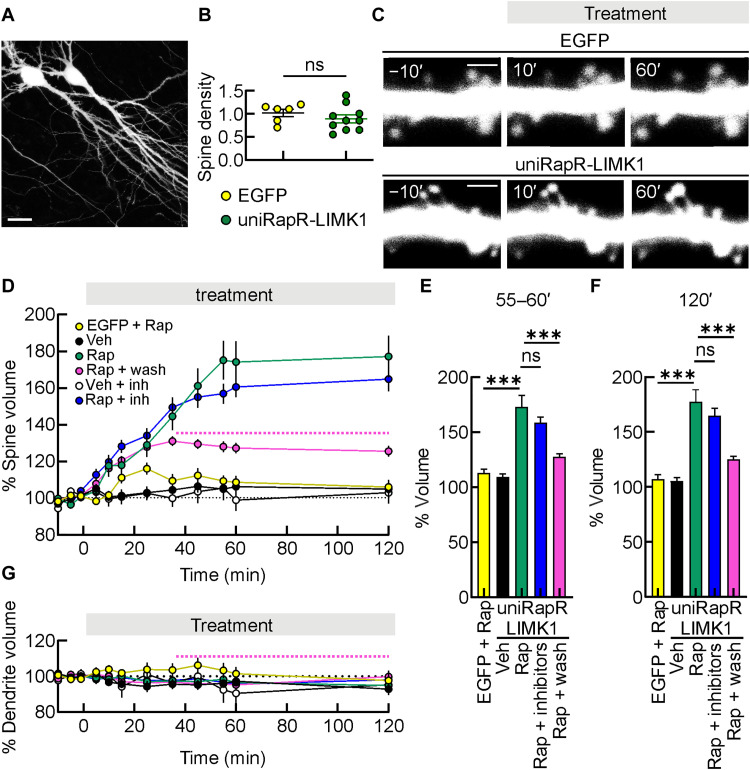
Fig. 3. Enlargement of dendritic spines induced by engineered LIMK1 activation in hippocampal organotypic slice cultures.
(A) A representative two-photon image of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in organotypic slice cultures. Scale bar, 25 μm. (B) Spine density in neurons transfected with unimolecular rapamycin regulatable domain (uniRapR)–LIMK1 and enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). ns, not significant; unpaired Student’s t test. (C) A series of two-photon images in a dendrite of an EGFP-transfected neuron (top) and in a dendrite of a neuron transfected with uniRapR-LIMK1 + EGFP (bottom), both before and after the application of Rap. Scale bars, 2 μm. (D) Mean time courses of spine volume obtained in EGFP-transfected neurons treated with Rap (yellow circles, EGFP + Rap), uniRapR-LIMK1 + EGFP-transfected neurons treated with Veh (black circles), Rap (green circles), Rap for 30 min before washout with artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) (pink curve, the dashed line indicates the washout), Veh in slices pretreated with a combination of KN93, IPA3, and GSK429286A (white circles, Veh + inh), and Rap in slices pretreated with a combination of KN93, IPA3, and GSK429286A (blue circles, Rap + inhibitors). (E and F) Bar graphs show the percentage of dendritic spine increments after 55 to 60 min (E) or 120 min (F) of Rap application. (G) Mean time courses of dendrite volume obtained in conditions shown in (D). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. ***P < 0.001. Statistics by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with the Dunnett’s post hoc test comparisons.