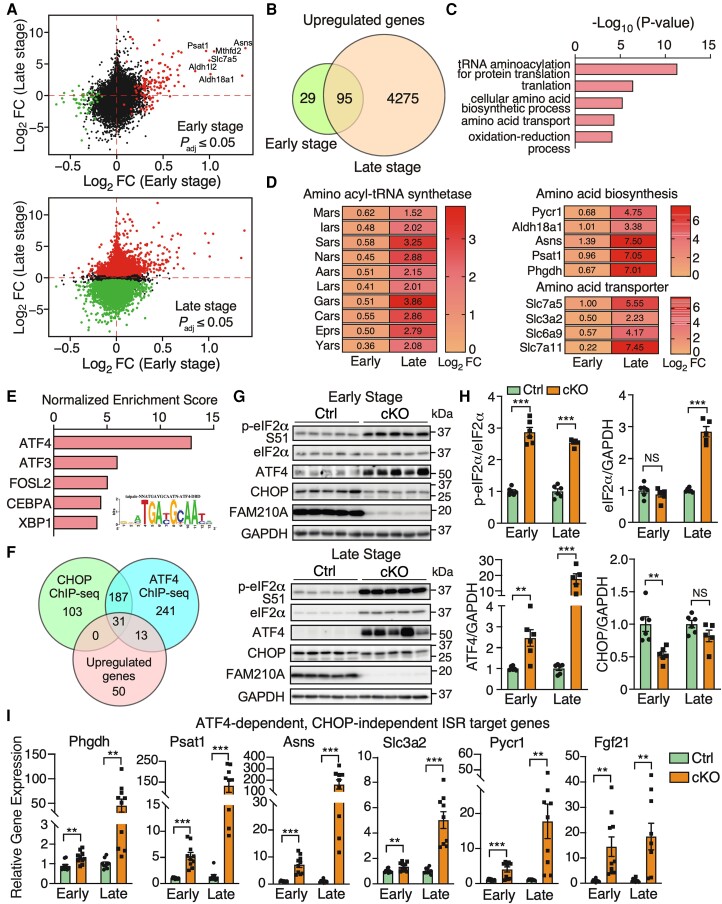
Figure 5.
Cardiomyocyte-specific FAM210A deficiency leads to persistent activation of ATF4-dependent CHOP-independent integrated stress response. (A) Differentially expressed genes at the transcriptomic level at the early (top) and late stages (bottom). (B) The Venn diagram illustrates the overlap of up-regulated genes at the RNA level in Fam210a cKO hearts at the early and late stages. (C) GO analysis using the Enrichr web tool suggests enhanced amino acid metabolism-related gene expression in cKO hearts. (D) Expression heat map of the differentially expressed genes from top three GO terms in (C). (E) iRegulon analyses identified ATF4 as the top transcription factor with the most enriched regulatory motif in all the 95 genes [from (B)] in the inset. (F) Overlapping up-regulated genes with CHOP and ATF4 ChIP-Seq databases reveals ATF4-regulated target genes in CMs. (G) Western blot detection of phospho-eIF2α, ATF4, and CHOP at the early and late stages of cKO hearts. (H) Quantification of protein expression as shown in (G). n = 6 for Ctrl and cKO at the early stage. n = 6 for Ctrl and n = 5 for cKO at the late stage. (I) Relative RNA expression of ATF4-dependent, CHOP-independent ISR downstream targets in cKO hearts at the early and late stages. β-Actin was used as a normalizer. n = 5M + 5F for Ctrl and cKO at the early stage. n = 5M + 4F for Ctrl and cKO at the late stage. NS, not significant; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t-test (H and I).