Extended Data Fig. 2. High G-to-A sequences with more than 20 private mutations identified from a Nextclade alignment of all available SARS-CoV-2 sequences.
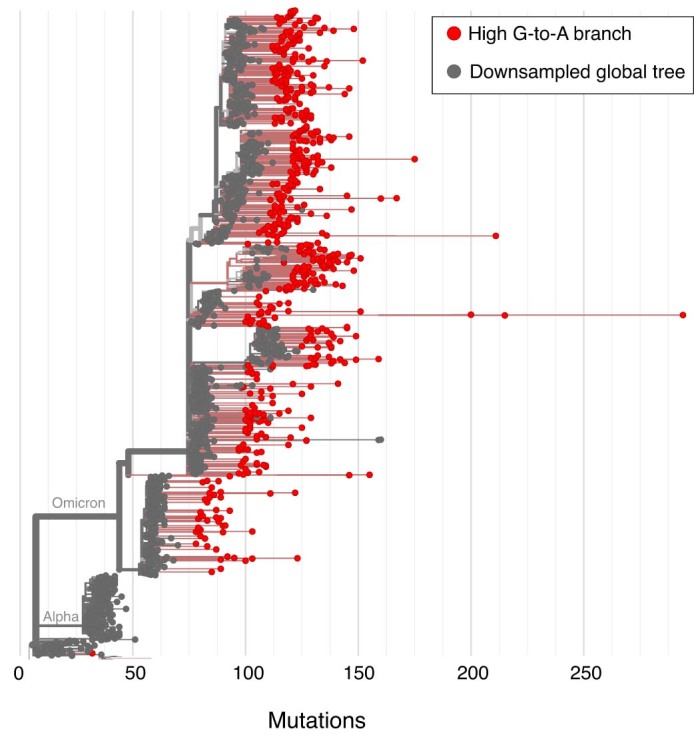
Nextclade was used to align sequences and identify private mutations. High G-to-A branches were identified on the basis of unlabelled private mutations. Usher.bio was then used to create a tree with high G-to-A branches highlighted on a downsampled global tree, with visualisation performed with Nextstrain.
