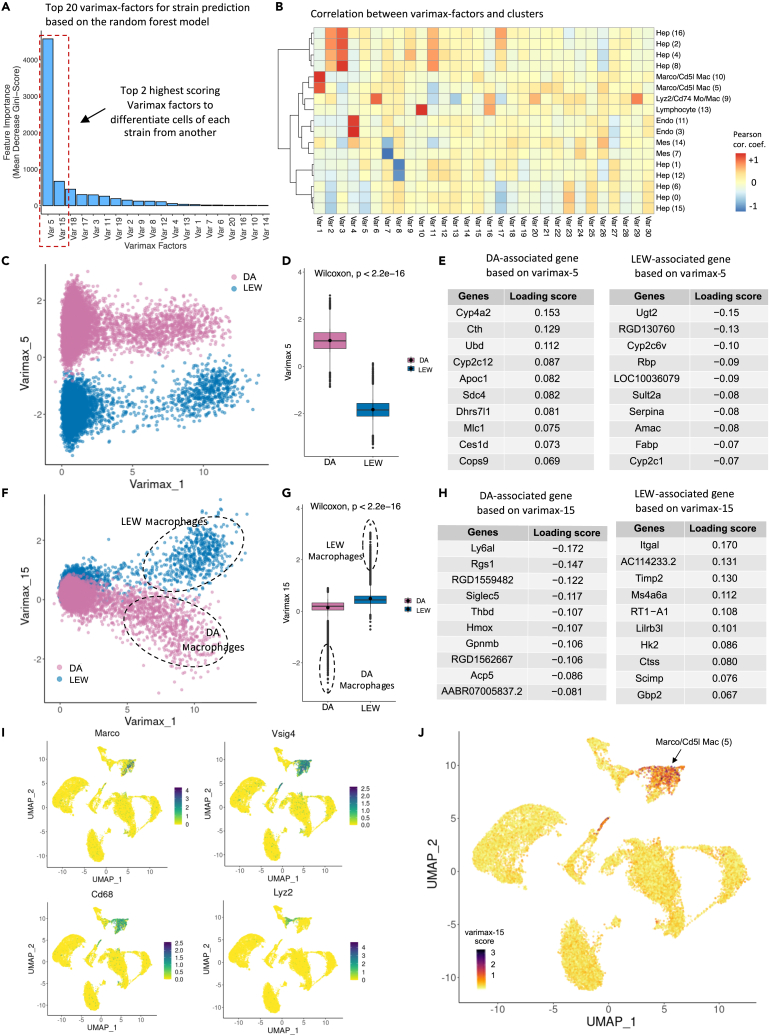
Figure 4.
Varimax PCs capture rat hepatic cell identity signatures and strain-specific differences
(A) Bar plot representing the feature importance scores (mean decrease Gini impurity) of the top 20 features (varimax factors) of the random forest model trained to predict the strain attributes of the rat hepatic cells. Varimax PC5 and 15 are the most informative features to differentiate cells of each strain from another, which indicates the two factors have captured strain-related variations within the map.
(B) A correlation heatmap between the average gene expression of each cluster and the loading scores of varimax factors (capturing the contribution of all genes to a factor). Columns are varimax factors and rows are cell populations. Each cell-type cluster is defined by key marker genes, and dark red or blue indicates that the expression of a marker gene set is positively or negatively correlated, respectively, with a particular varimax factor. A high absolute correlation value indicates a match between a varimax factor and a cell-type cluster.
(C) The projection of cells over varimax-1 and 5 indicates that the cells from each strain form distinct clusters over varimax-5.
(D) Boxplot indicating the distribution of varimax-5 score over each strain. Cells from DA and LEW strains represent significantly different varimax-5 scores (Wilcoxon-test p value <2.2e-16), indicating that varimax-5 has captured strain differences.
(E) The top 10 genes on the top (left table) and bottom (right table) of the varimax-5 loading list mainly contain known hepatocyte markers, indicating that varimax-5 has captured hepatocyte-specific strain differences. Genes with high positive scores (left table) are associated with the DA strain and genes indicating negative loading scores (right table) are LEW-related. The absolute loading scores indicate the contribution of each gene to the corresponding factor.
(F) Projection of cells over varimax-1 and 15 indicates that a population of cells from each strain (dotted lines) forms distinct clusters over varimax-15. Annotation of the selected cells indicates that they are mainly from the Marco+ myeloid cluster 5.
(G) Boxplot indicating the distribution of hepatic cells based on strain over varimax-15. (Wilcoxon-test p value <2.2e-16). The outlier data points (dotted lines) are mainly myeloid cells.
(H) The top 10 genes with positive (right table) and negative (left table) varimax-15 loading scores are immune-response related. Genes with positive scores (right table) are associated with the LEW strain, and genes indicating negative loading values (left table) are DA related. The absolute loading scores indicate the contribution of each gene to the corresponding factor.
(I) Expression pattern of known myeloid marker genes Marco, Vsig4, Cd68, and Lyz2 over UMAP. Dark green represents high expression values. The distribution of general myeloid markers (Cd68, Vsig4) and non-inflammatory myeloid marker (Marco) is consistent with the varimax-15 distribution (Figure 2J).
(J) The UMAP projection of cells colored based on the varimax-15 score shows the enrichment of varimax-15 over Marco+ myeloid population (cluster 5). Darker colors represent higher values of varimax-15 scores. Data are represented as mean ± SEM with each dot representing a single cell. Corrcoef.: correlation coefficient, Var: varimax PC. varimax PCs are referred to as PCs within the main text.