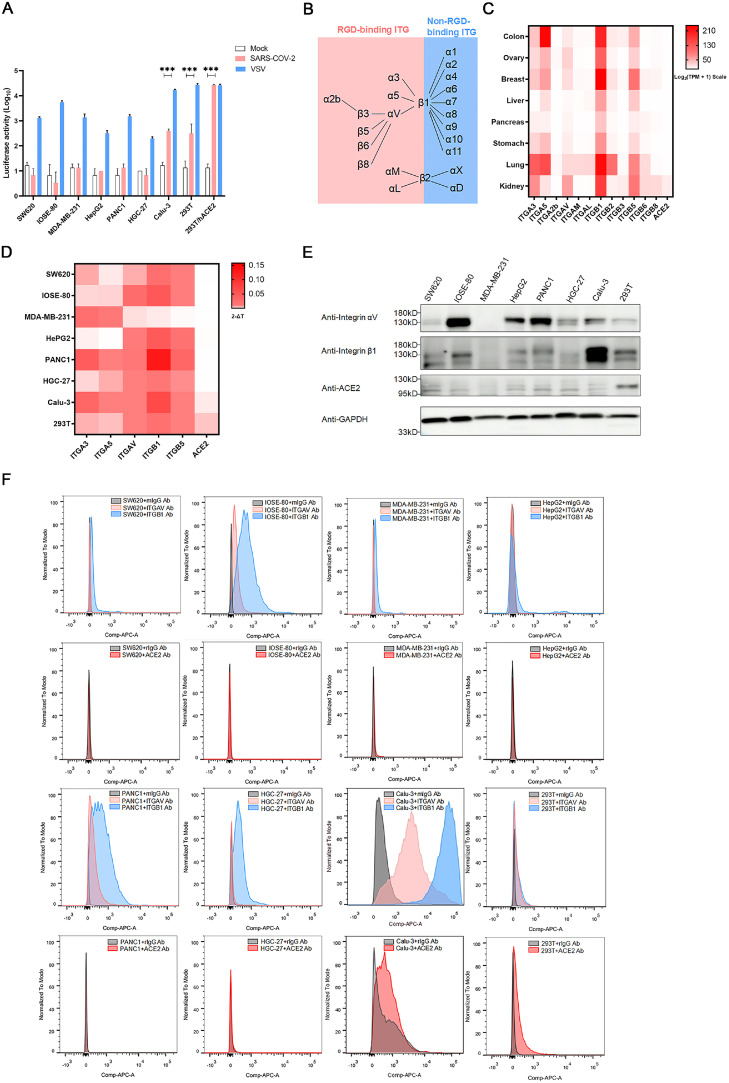
Fig. 1.
The high expression of integrin αvβ1 in the SARS-CoV-2 susceptible cell lines.
A. Entry of SARS-CoV-2 S pseudotyped virions into human cell lines SW620, IOSE-80, MDA-MB-231, HepG2, PANC-1, HGC-27, BEAS-2B, Calu-3, 293T, and 293T/hACE2). Cells were infected with SARS-CoV-2 S-pseudotyped (red) and VSV-pseudotyped viruses, respectively, or mock infection (white). At 72 h post infection, viral entry efficiency was measured by luciferase activity assay. Significant difference from mock were determined by two-tailed unpaired t-test. ***P < 0.001. Error bars indicate SD (n = 3).
B. A schematic diagram showing the RGD- and non-RGD binding integrins.
C. Heatmap of the mRNA expression profile of RGD-binding integrins in different human organs obtained from the GEPIA2 database. The mRNA expression was exhibited by Log2(TPM+1) scale, and TPM denotes Transcripts Per Million.
D. Heatmap of the mRNA expression profile of integrin ITGA3, A5, AV, B1, B5, and ACE2 in indicated cell lines detected by RT-qPCR. The mRNA expression levels were normalized to the level of GAPDH.
E. The protein expression level of integrin ITGAV, B1, and ACE2 in indicated cell lines was analyzed by western blot with anti-integrin av, β1, and ACE2 antibodies, respectively.
F. The expression levels of ITGAV and ITGB1 on the cell membrane were analyzed by flow cytometry. Histograms indicate the expression of integrins. Red: anti-ACE2 Ab, pink: anti-integrin av Ab, blue: anti-integrin β1 Ab, gray: isotype-control Ab.