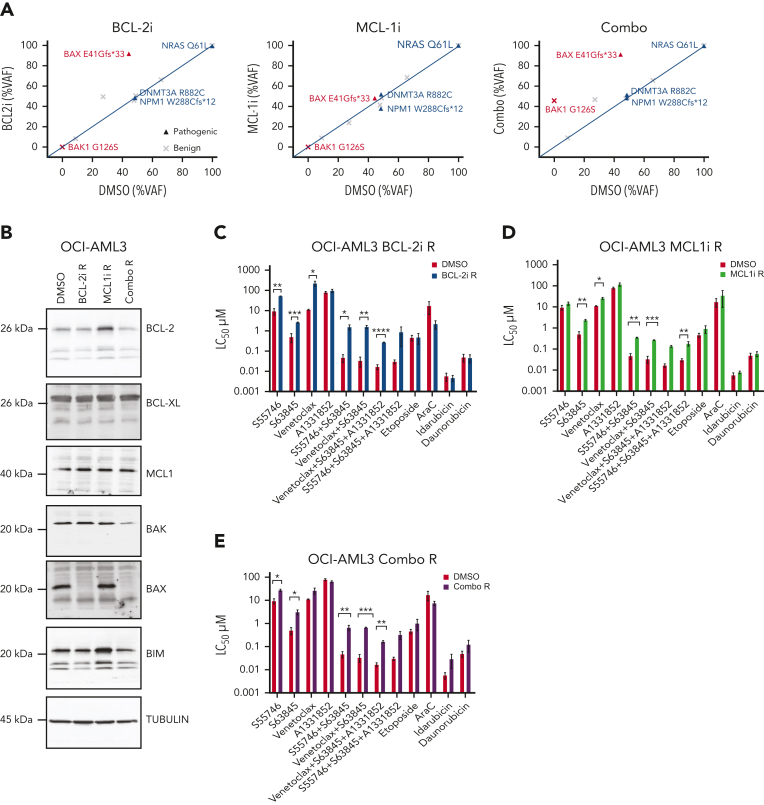
Figure 3.
Acquired resistance to BH3-mimetics selects for BAX loss in vitro. (A) VAF of indicated variants in OCI-AML3 cells with acquired resistance to BH3-mimetics compared with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) control. OCI-AML3 cells, which harbor a naturally occurring BAX E41Gfs∗33 abnormality were continuously passaged with progressively higher concentrations (maximum 3 μM) of BCL-2i resistant (BCL-2i-R), MCL1i resistant (MCL1i-R), or combined BCL-2i-R and MCL1i-R (combo R). Cells were then treated in the absence of drug(s) for 6 weeks and BAX targeted amplicon sequencing was performed and compared with DMSO control. (B) Immunoblot profiling of BCL-2 family proteins in OCI-AML3 cultures tolerant to 3 μM of drug (DMSO, BCL-2i-R, MCL1i-R, or combo R). (C-E) Sensitivity of BH3-mimetic resistant (tolerant to 3 μM) OCI-AML3 cells to various drugs and combinations. OCI-AML3 DMSO control, BCL-2i-R, MCL1i-R, or combo R cells were treated with the indicated drugs as single agents or in equimolar combination (0.001-10 μM). Sensitivity was expressed as the 50% lethal concentration (LC50 μM) determined by flow cytometry after 48 hour-exposure. Error bars are standard deviation (SD) of 3 independent experiments. ∗P < .05, ∗∗P <.01, and ∗∗∗P < .001.