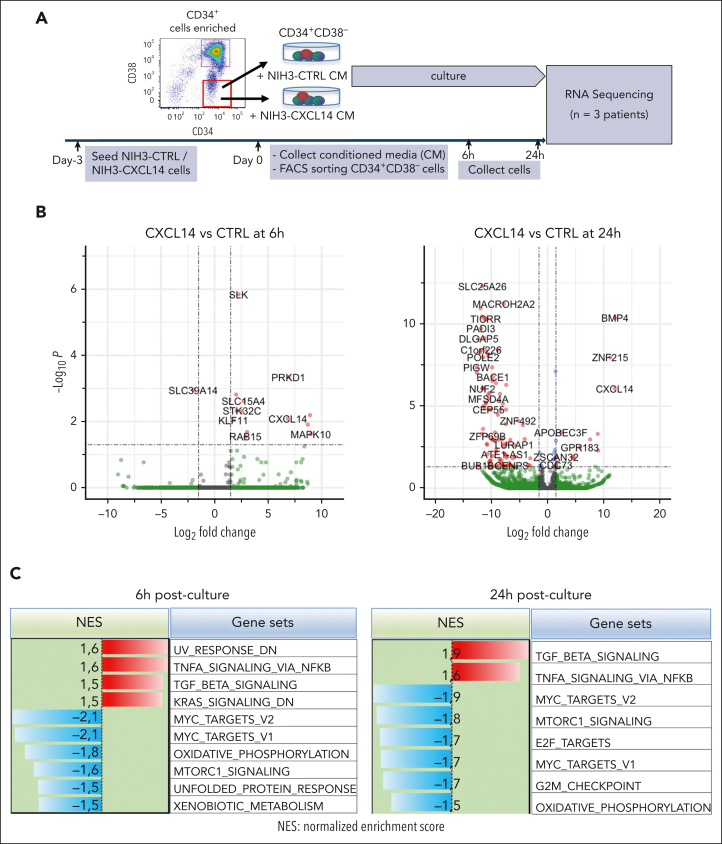
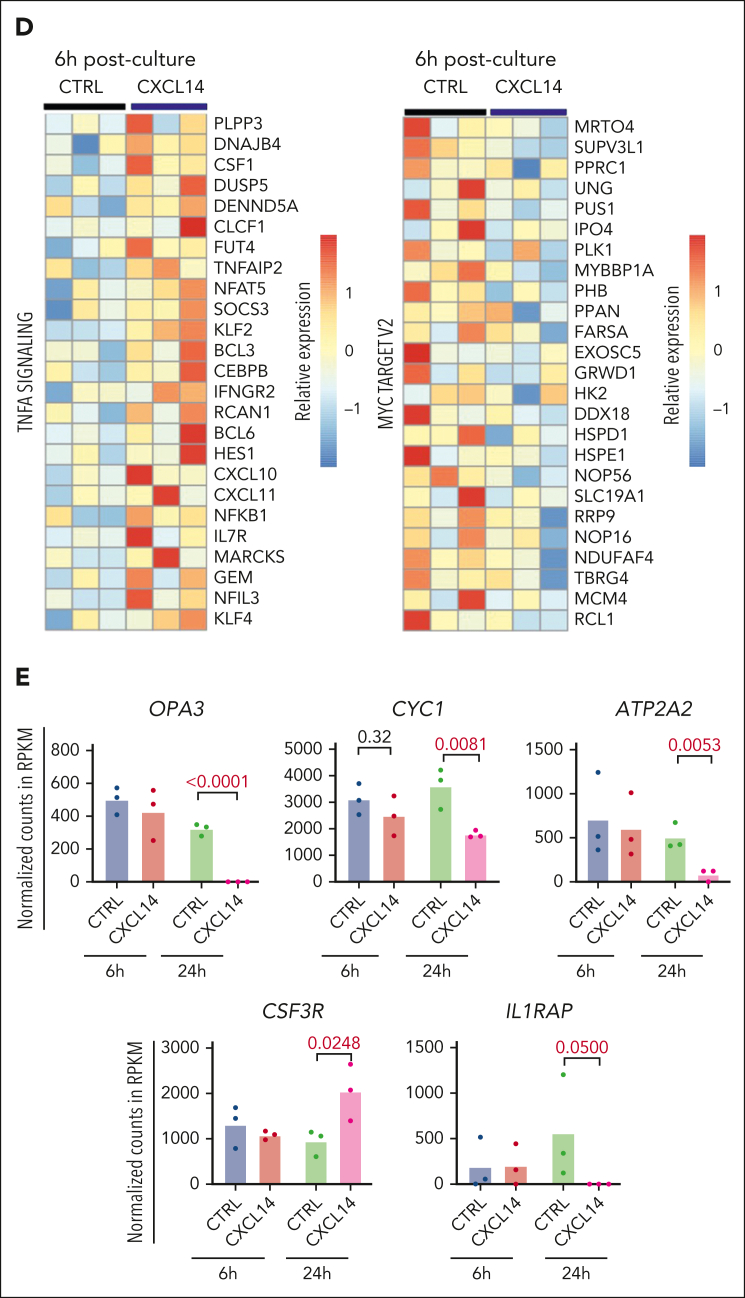
Figure 6.
RNA sequencing reveals molecular changes in CML LSCs after CXCL14 stimulation. (A) Experimental setup. CML CD34+CD38– cells from the BM of patients with CML were sorted and cultured with conditioned media derived from NIH3-CXCL14 or NIH3-CTRL. The CML cells were collected at 6 and 24 hours and sorted directly into lysis buffer for subsequent RNA sequencing. Data were from 3 independent experiments with 3 patients with CML. (B) Volcano plots showing differentially expressed genes in the CML LSCs 6 hours and 24 hours after stimulation with CXCL14-CM compared with that with the control BM. FDR-q value represents the false discovery rate of the P values. (C) The upregulated and downregulated gene sets in the CML CD34+CD38− cells at 6 hours (left) and 24 hours (right) after stimulation with CXCL14-CM. Data are from 3 independent sorting experiments on 3 patients with CML. (D) The heatmap showing the top 25 dysregulated genes within the enriched gene sets of tumor necrosis factor alpha signaling and MYC targets_V2 in the CML CD34+CD38− cells at 6 hours after stimulation with CXCL14-CM. (E) RNA sequencing shows expressions of outer mitochondrial membrane lipid metabolism regulator (OPA3), cytochrome c1 (CYC1), ATPase sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ transporting 2 (ATP2A2), colony stimulating factor 3 receptor (CSF3R), and IL-1 receptor accessory protein (IL1RAP) in the CD34+CD38– cells at 6 hours and 24 hours after stimulation with CXCL14. The numbers in the panels are P values determined by unpaired t test. See also supplemental Figure 9. RPKM, reads per kilobase of transcript, per million mapped reads.