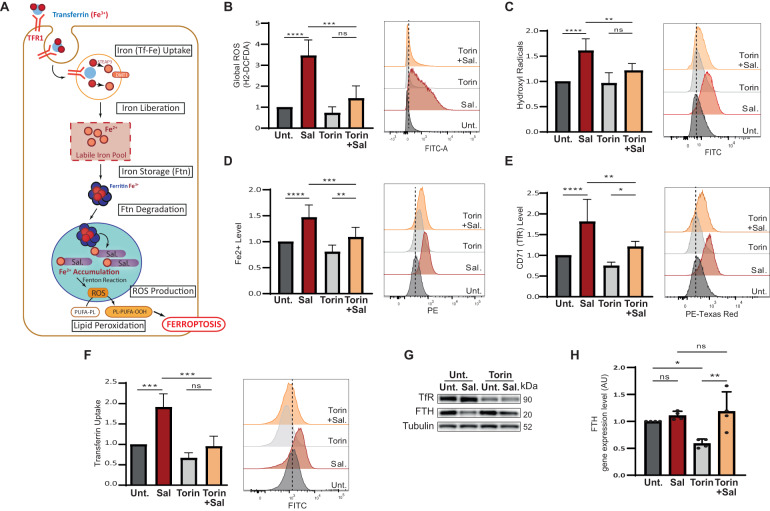
Fig. 2. mTOR inhibition reduces pro- ferroptotic hallmarks induced by Sal.
A Iron entry into the cell is mediated by the binding of Fe3+-Tf complex to TFR and its subsequent endocytosis. Iron is released under the acidic environment of the endosome, and is reduced to Fe2+ by STEAP3 and transported into the cytosol by DMT1. Free iron, constituting the labile iron pool, can be used (in mitochondria, …), exported, or stored in ferritin. Low iron availability triggered the degradation of ferritin in mitochondria. Salinomycin sequestered iron in the lysosomes, triggering a cellular iron-depletion response that induced an increase in iron entry, and an increase ferritin degradation, it results in an accumulation of iron in the lysosome and a subsequent massive ROS production (by the Fenton reaction) leading to a considerable lipid peroxidation and ultimately cell death. B–G HMLER CD24L were treated with Sal, Torin, or a combination of both for 48 h. B Global ROS level determined by H2-DCFDA staining coupled with FC (n = 4). C Hydroxyl Radical level determined by HPF staining coupled with FC (n = 6). D Fe2+ level determined by FerroOrange staining coupled with FC (n = 9). E TFR level determined by anti-CD71 staining coupled with FC (n = 7). F Transferrin Uptake was determined by Alexa-488-Transferin staining coupled with FC (n = 4). G Immunoblotting for the indicated iron-related protein. Tubulin is used as loading control. H FTH gene expression level by RT-qPCR. Data are presented as: mean ± SD, ANOVA test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.