FIGURE 3.
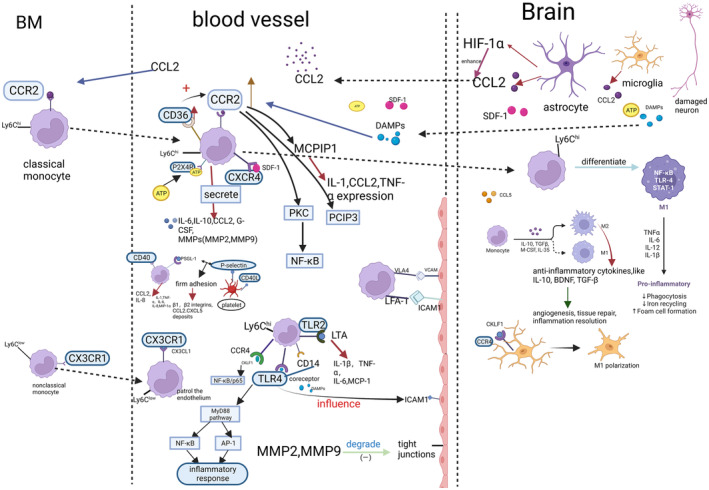
Cytokines/chemokines involved in the recruitment and migration of monocytes in ischemic stroke. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; BDNF, brain‐derived neurotrophic factor; BM, bone marrow; CCL, C‐C motif chemokine ligand; CCR, C‐C motif chemokine receptor; CKLF1, chemokine‐like factor 1; CX3CL, C‐X3‐C motif chemokine ligand; CX3CR, C‐X3‐C motif chemokine receptor; CXCL, C‐X‐C motif chemokine ligand; CXCR, C‐X‐C motif chemokine receptor; DAMP, damage‐associated molecular pattern; G‐CSF, granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor; HIF‐1α, hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1‐alpha; ICAM, intercellular adhesion molecule‐1; IL, interleukin; LFA, lymphocyte function‐associated antigen 1; Ly6C, lymphocyte antigen 6C; MCP‐1, monocyte chemotactic protein‐1; MCPIP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein‐1 induced protein 1; M‐CSF, macrophage colony‐stimulating factor; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐kappa B; P2X4R, purinergic receptor P2X4; PKC, protein kinase C; PSGL‐1, P‐selectin glycoprotein ligand‐1; SDF, stromal cell‐derived factor; STAT1, signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; TGF‐β, transforming growth factor‐beta; TLR, Toll‐like receptor; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐alpha; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule; VLA, very late activation antigen.
