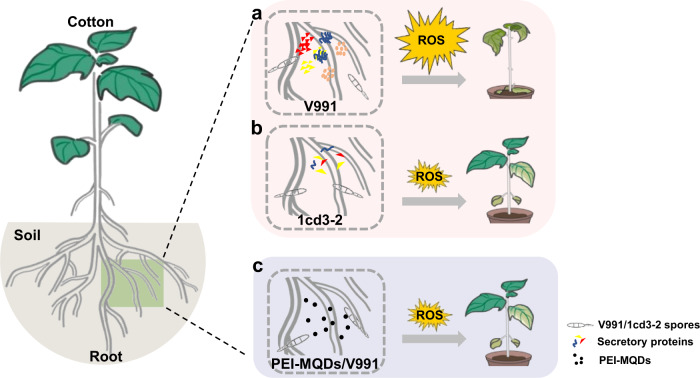
Fig. 6. The interaction model between V.dahliae and cotton.
a V991 regulates expression of more virulence-related genes during the host interaction, causing excessive accumulation of ROS in cotton and leading to severe disease. b 1cd3-2 expressed fewer virulence-related genes during the host interaction, resulting in lower accumulation of ROS in cotton and ultimately a milder phenotype of disease. c PEI-MQDs increase resistance to V991 by maintaining ROS homeostasis in cottons.