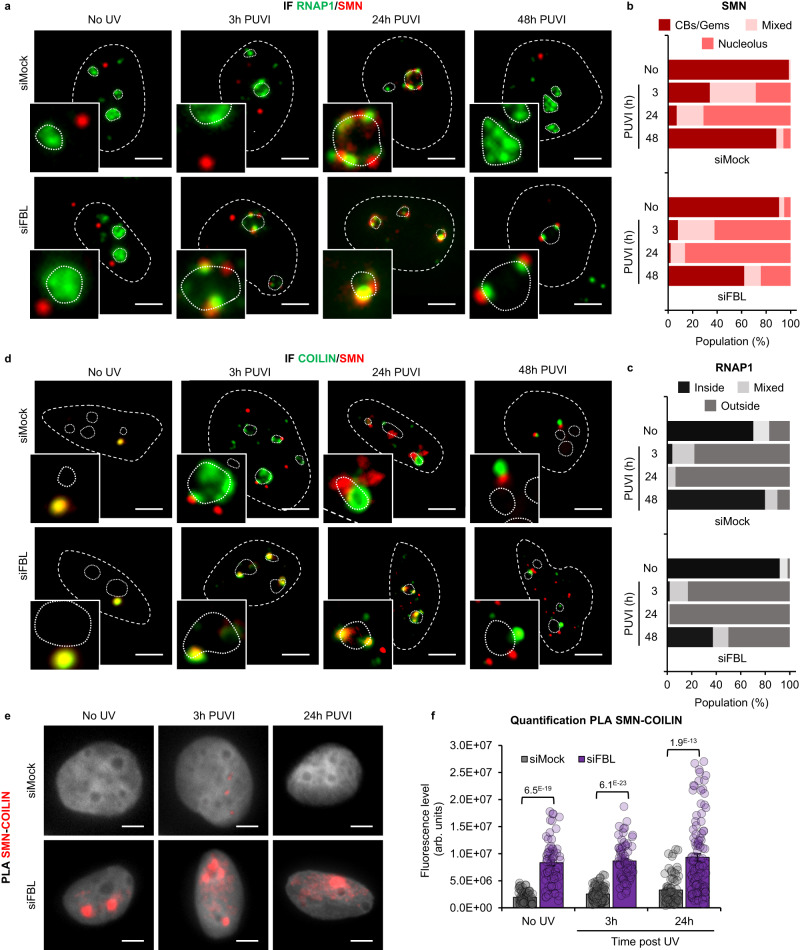
Fig. 5. The release of SMN from the nucleolus is FBL-dependent.
a, d Representative microscopy images of immunofluorescence (IF) assay showing the localization of SMN (red) and (a) RNAP1 or (d) COILIN (green) at different times Post UV-Irradiation (PUVI) in cells transfected with siMock or siFBL pool. Nuclei and nucleoli are indicated by dashed and dotted lines respectively. Scale bar: 5 µm. b, c Quantification of cells number for localization of (b) SMN (in Cajal Bodies [CBs] or Gems, at the periphery of the nucleolus or mixed localization) and (c) RNAP1 (inside the nucleolus, outside the nucleolus or mixed localization) at different times PUVI in cells transfected with siMock or siFBL pool. At least 80 cells from one representative experiment were analyzed. e Representative microscopy images of Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA) in red showing the interaction between SMN and COILIN at different times PUVI in cells transfected with siMock or siFBL pool. Scale bar: 5 µm. DAPI in grey. f Quantification of fluorescent signal in the nucleus against the couple SMN-COILIN from PLA experiment in cells transfected with siMock or siFBL pool after UV-C irradiation. Data are represented as mean values +/− SEM. At least 65 cells was quantified from one representative experiment. The p-value correspond to a student’s test with two-tailed distribution and two-sample unequal variance to compare siFBL with siMock. Source data of graphs are provided as a Source Data file.