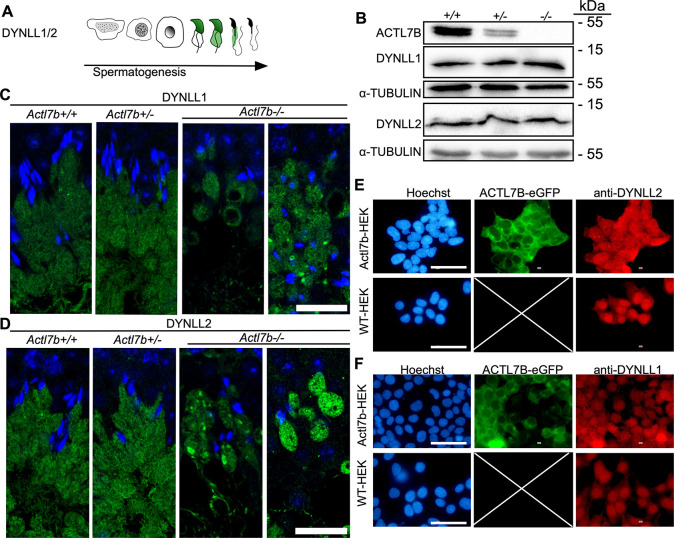
Fig. 7.
Localization of DYNLL1 and DYNLL2 in Actl7b-deficient testis. (A) Graphical depiction of DYNLL1 and DYNLL2 immunolocalization during spermiogenesis based on literature (Wang et al., 2005). (B) Western blots on protein extracts from whole Actl7b+/+, Actl7b+/− and Actl7b−/− testis. Anti-ACTL7B, anti-DYNLL2 and anti-DYNLL2 were used. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. (C) DYNLL1 staining in Actl7b+/+, Actl7b+/− and Actl7b−/− elongating spermatids. DAPI was used as a counterstain. Scale bar: 20 µm. (D) DYNLL2 staining in Actl7b+/+, Actl7b+/− and Actl7b−/− elongating spermatids. DAPI was used as a counterstain. Scale bar: 20 µm. (E) Immunocytochemical staining against DYNLL2 in wild-type and ACTL7B-eGFP-expressing HEK cells. Scale bars: 50 µm. (F) Immunocytochemical staining against DYNLL1 in wild-type and ACTL7B-eGFP-expressing HEK cells. Scale bars: 50 µm. Images shown in E and F are taken from the overviews displayed in Figs S11 and S12.