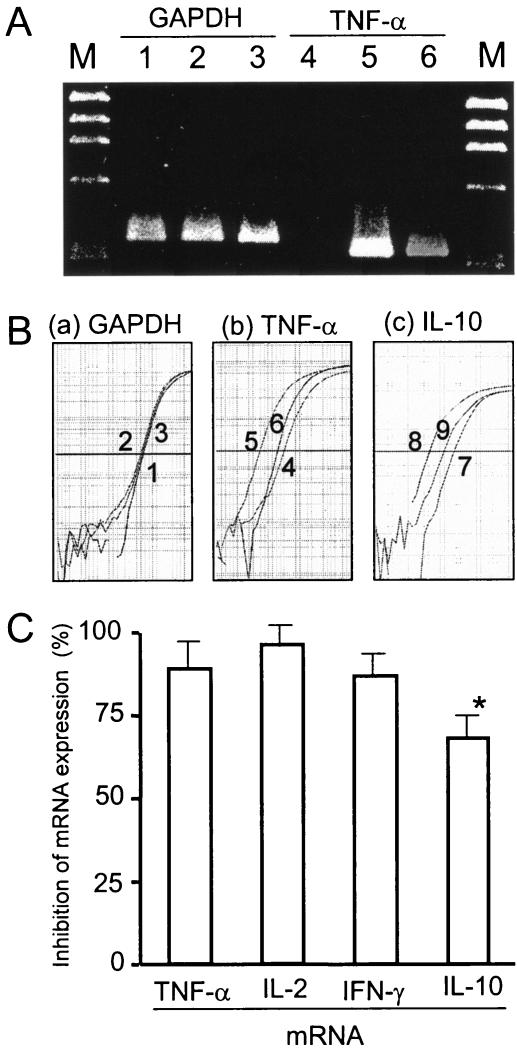
FIG. 5.
Suppression of TSST-1-induced cytokine mRNA expression by anisodamine. (A) Effect of anisodamine on TNF-α mRNA expression was examined by RT-PCR. Human PBMCs (2.5 × 106 cells) were stimulated with TSST-1 (10 ng/ml) for 3 h in the presence or the absence of anisodamine (50 μg/ml). After incubation, the PBMCs were procured and total cellular RNA was extracted. mRNA was reverse transcribed and amplified by PCR with cytokine-specific primers. RT-PCR products: lanes 1 to 3, the housekeeping gene GAPDH; lanes 4 to 6, the TNF-α gene; lanes 1 and 4, no TSST-1 stimulation; lanes 2 and 5, TSST-1 stimulation; lanes 3 and 6, TSST-1 stimulation in the presence of anisodamine; lanes M, molecular size marker (HaeIII-digested φX174 replicative-form DNA fragments). (B, parts a and b) Experiments similar to those for TNF-α gene expression whose results are shown in panel A were performed by a real-time PCR assay. The relative copy numbers of the gene sequences for GAPDH (a) and TNF-α (b) were estimated as described in Materials and Methods. Samples 1 to 6 correspond to those in lanes 1 to 6 in panel A. (B, part c) IL-10 gene expression examined by a real-time PCR assay, as described above. Sample 7, no TSST-1 stimulation; sample 8, TSST-1 stimulation; sample 9, TSST-1 stimulation in the presence of anisodamine. (C) On the basis of the relative copy numbers obtained in the experiment whose results are shown in panel B, the percent inhibition of TNF-α and IL-10 mRNA expression by anisodamine was calculated and is shown. Experiments similar to the experiments whose results are shown in panel B were performed with IL-2 and IFN-γ, and the percent inhibition by anisodamine was evaluated and is also shown. *, P < 0.05 compared with the data for the proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-2, and IFN-γ).