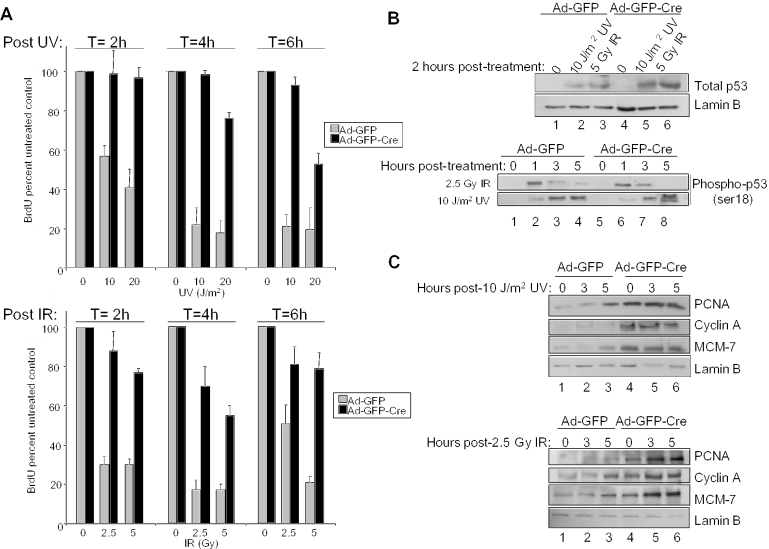
Figure 2.
Acute RB loss compromises the rapid checkpoint response to UV and IR. (A) Top panel: Ad-GFP and Ad-GFP-Cre infected MAFs were exposed to 0, 10 or 20 J/m2 UV and cultured for 2, 4 or 6 h in the presence of BrdU for the final 2 h. Immunofluorescence was utilized to detect BrdU labeled nuclei, which were then scored and represented as percent untreated control. Bottom panel: the aforementioned experiment was repeated following treatment with 0, 2.5 or 5 Gy IR. (B) To assess the role of RB in rapid DNA damage signaling, asynchronously growing MAFs infected with either Ad-GFP or Ad-GFP-Cre were exposed to 2.5 Gy IR or 10 J/m2 UV, and harvested at various time points in RIPA buffer. Equal amounts of protein were separated by electrophoresis and immunoblotting for total p53 (top panel) and phosphorylated p53 (ser-18) (bottom panel) (C) To analyze the role of RB in DNA damage signaling to downstream targets, cells were treated and harvested as in (B) and immunoblotting for PCNA, cyclin A and MCM-7 (top and bottom panels) was performed. Lamin B serves as a control for equal loading.