Figure 1:
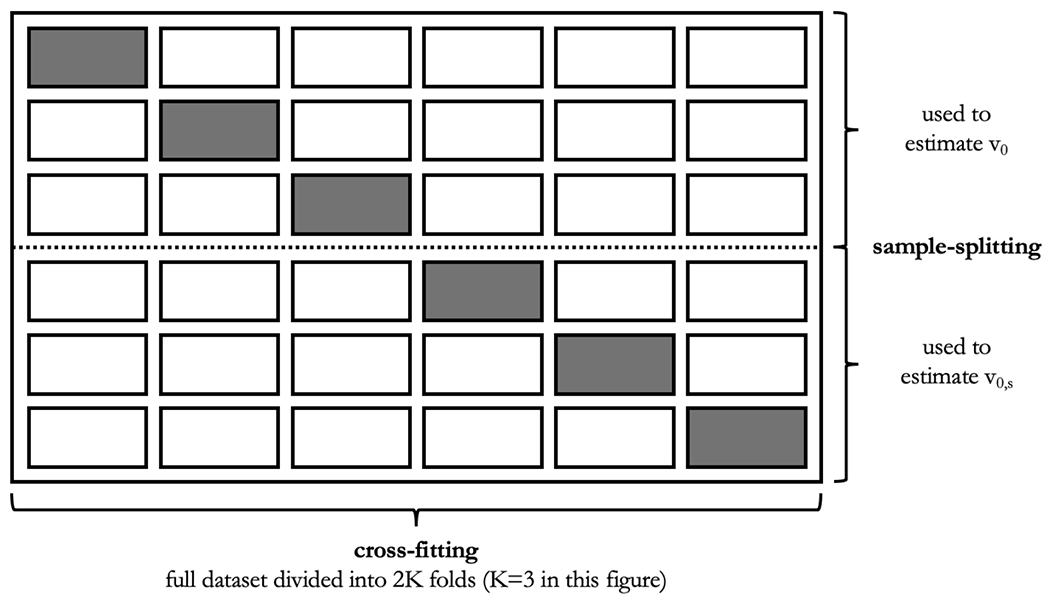
Illustration of dataset subdivision when sample-splitting and cross-fitting are used simultaneously for valid inference under the zero-importance hypothesis (sample-splitting) without requiring Donsker class conditions (cross-fitting). Each row represents the entire dataset with a different subset singled out (in grey) as testing set. To estimate v0, the top three rows are used. In each such row, f0 is estimated using data in the white cells, and v0 is estimated using the resulting estimate of f0 and data in the grey cells. Row-specific estimates of v0 are then averaged. The process is repeated for estimating v0,s but instead using the bottom three rows and estimating f0,s rather than f0.
