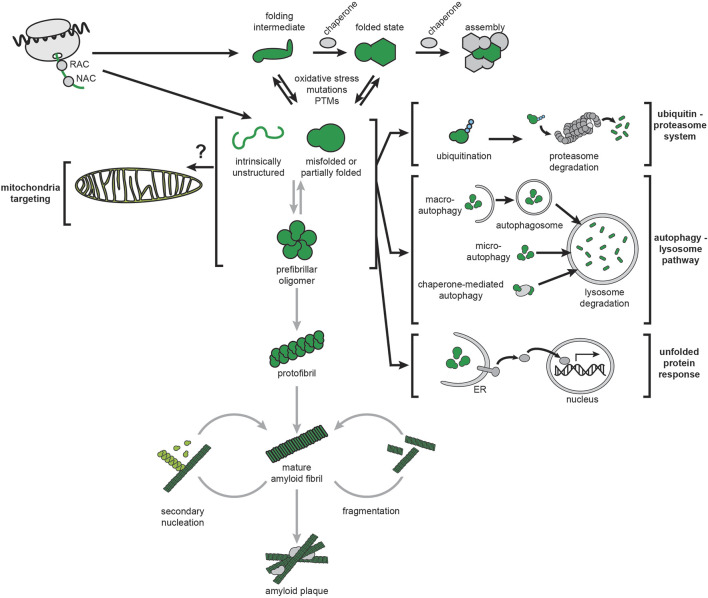
FIGURE 4.
Amyloids and cellular proteostasis. The proteostasis network of mammalian cells is depicted by black arrows. Chaperones that guide cotranslational folding on the ribosome include the nascent polypeptide-associated complex (NAC) and the ribosome-associated complex (RAC). Additional chaperones guide monomer folding and assembly into complexes. The ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) targets misfolded proteins, or proteins that are no longer needed, by ubiquitination and digestion by the proteasome. The autophagy-lysosome pathway (ALP) targets misfolded proteins (and larger structures such as large aggregates and organelles) by delivering them to the lysosome via distinct pathways (macroautophagy, microautophagy and chaperone-mediated autophagy). Protein unfolding stress can activate complex signal transduction pathways leading to gene expression changes for restoring protein homeostasis, most notably the ER-based unfolded protein response (UPRER). Amyloidogenesis, depicted by gray arrows, can initiate from intrinsically disordered or misfolded structures and proceed by stepwise formation of oligomers, protofibrils, and finally mature fibrils. It can also be accelerated by secondary nucleation and fragmentation of existing fibrils.