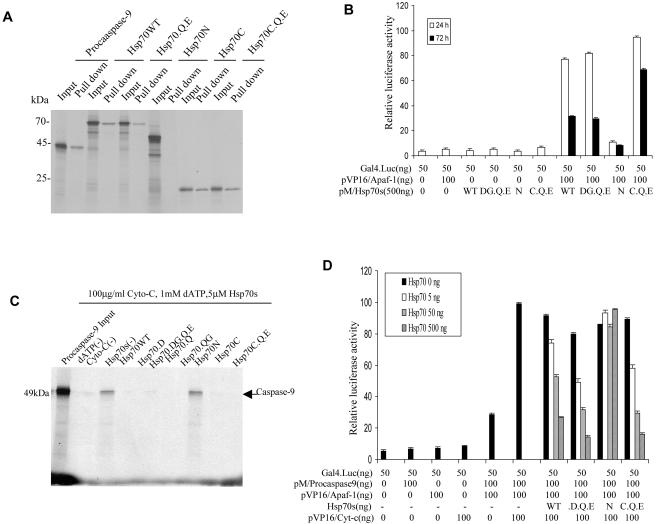
Fig 6.
Hsp70 mutants retain the ability to intact with Apaf-1 and inhibit the interaction between procaspase-9 and Apaf-1. (A) Hsp70 and its mutants interact with Apaf-1 in vitro. Equal amounts of Apaf-1, previously immobilized on Ni2+ beads, were incubated with 3 μL of 35S-labeled wild-type Hsp70 protein (Hsp70WT) and its mutants in binding buffer for 30 minutes at 25°C. 35S-labeled procaspase-9 was used as a positive control (first 2 lanes). The mixtures were washed and analyzed by 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). (B) In vivo assays: mammalian 2-hybrid experiments were performed in Cos-1 cells cotransfected with the indicated plasmids. Luciferase activity was measured as described. (C) In vitro assays: three μL of 35S-labeled procaspase-9 and 0.5 μM Apaf-1 previously immobilized on Ni2+ beads were incubated in binding buffer for 30 minutes at 25°C and then incubated with or without cytochrome c and deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) in the presence or absence of Hsp70WT or its mutants for 3 hours at 4°C. The mixtures were washed and then analyzed by 10% SDS-PAGE. (D) Hsp70 and its mutants interact with Apaf-1 in vivo. Cos-1 cells were cotransfected with Gal 4-Luc and the indicated plasmids. Luciferase activity was measured as described