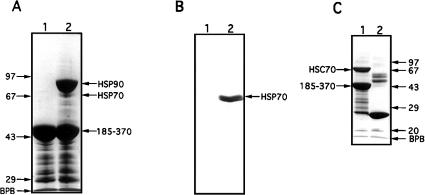
Fig 1.
Interaction of cytosolic heat shock protein (Hsp)70 and recombinant heat shock cognate (Hsc)70 with the C-terminal domain of cyclophilin 40 (CyP40). (A) Glutathione-agarose (40 μL) charged with glutathione S-transferase (GST)-bCyP40 185–370 (see Fig 2A) was incubated with rotation for 6 hours at 4°C with bovine myometrial cytosol (200 μL) prepared in binding buffer. After centrifugation, the gel was washed eight times with binding buffer, the first 4 washes containing 0.2% vol/vol Triton X-100. Retained proteins (lane 2) were extracted from the gel with sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) sample buffer and were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 10% wt/vol polyacrylamide gel followed by Coomassie blue staining. Fusion protein-charged gel not exposed to cytosol was used as control (lane 1). (B) A parallel study was performed as in (A) except that proteins separated by SDS-PAGE were electrotransferred to nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Boisciences) and immunoblotted with N27 (Hsp70) monoclonal antibody. (C) GST and GST-bCyP40 185–370 were immobilized on glutathione-agarose and the protein-charged gels (40 μL) were incubated as described in (A) with bacterial lysate (400 μL) containing recombinant Hsc70. Contaminating proteins were removed by washing, and retained proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 12.5% polyacrylamide gel followed by Coomassie blue staining. Proteins recovered with GST (control) are shown in lane 2. Protein molecular weight markers (Pharmacia) are shown on the left (panel A) and on the right (panel C). BPB, bromophenol blue