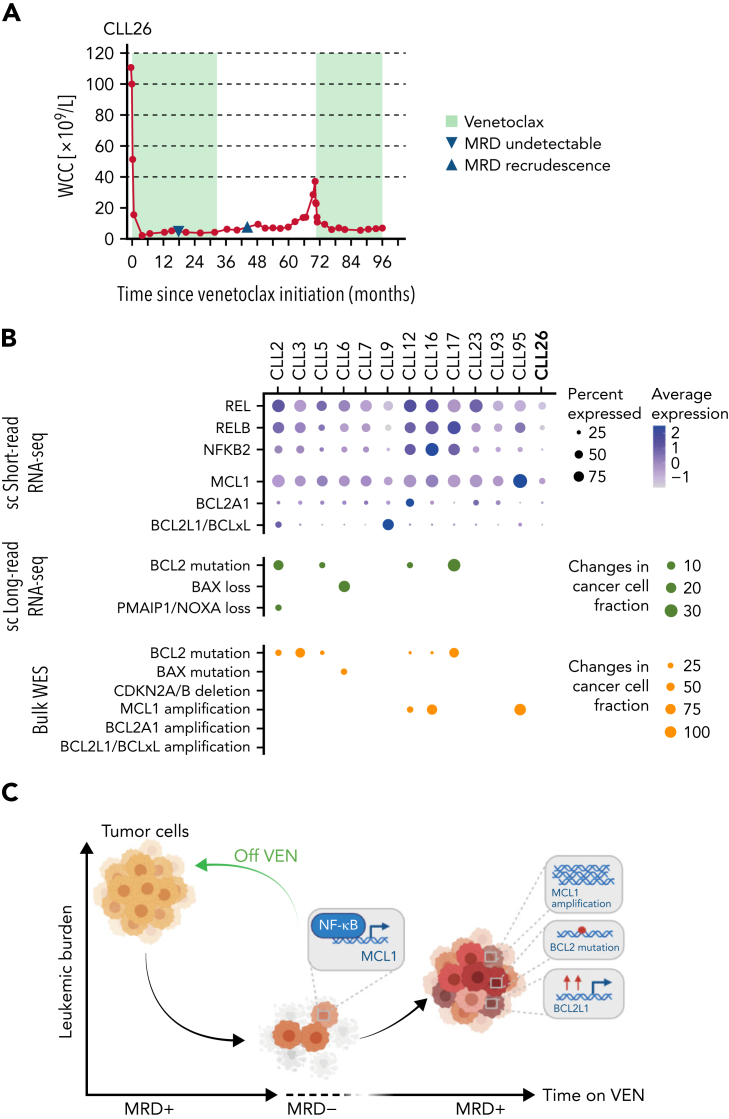
Figure 7.
Single-cell multiomics approach reveals multilayered changes driving VEN resistance. (A) PB white cell counts of CLL26 during VEN treatment, following VEN discontinuation, and subsequent VEN retreatment when CLL recurred. MRD undetectable: first confirmation of PB undetectable MRD (CLL cells <0.01% of leukocytes), MRD recrudescence: first confirmation of MRD positivity in PB (CLL cells ≥0.01% of leukocytes). MRD, measurable residual disease. (B) Dot plots summarizing the single-cell RNA-seq, single-cell long-read sequencing, and WES changes observed in patient samples at VEN-relapse. For the single-cell short-read RNA-sequencing, color indicates relative degrees of gene expression, and the size of the dot indicates the proportion of cells with altered expression in a patient sample. For single-cell long-read RNA-seq and WES, the size of the dot indicates the fraction of cells harboring the mutation in a patient sample; no dots: not detected. (C) Schematic illustration of the study highlights.