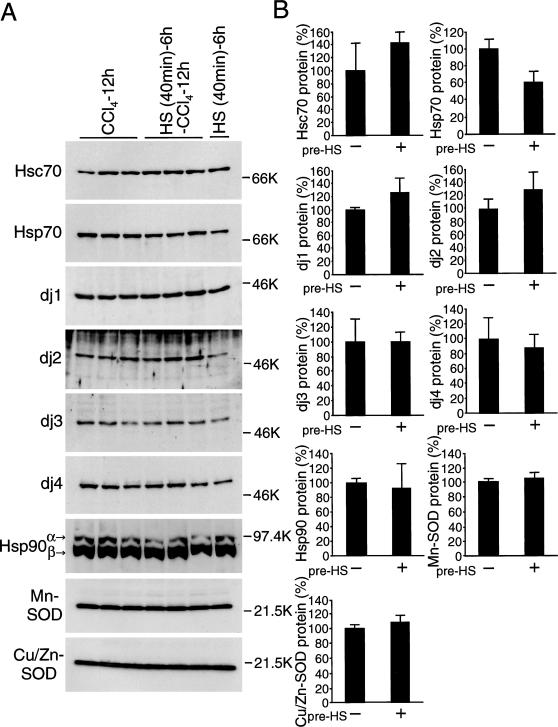
Fig 5.
Induction of heat shock protein (Hsp) 70 and DnaJ chaperones in the carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-treated rat liver with heat pretreatment. (A) and (C) Rats were heated at 42°C for 40 minutes and allowed to recover at room temperature for 6 hours or not heat treated. Next, CCl4 was given intraperitoneally or not given. After 12 hours (A) or 24 hours (C), liver extracts (10 μg of protein for heat shock cognate [Hsc] 70, Hsp70, dj1, dj2, Hsp90, Mn-superoxide dismutase [SOD], and Cu/Zn-SOD; 50 μg of protein for dj3 and dj4) were subjected to immunoblot analysis for Hsc70, Hsp70, dj1, dj2, dj3, dj4, Hsp90, Mn-SOD, and Cu/Zn-SOD. Molecular weight markers are phosphorylase B (97.4 kDa), bovine serum albumin (66 kDa), ovalbumin (46 kDa), and trypsin inhibitor (21.5 kDa). (B) and (D) The results of CCl4-treated rats with or without heat treatment in (A) and (C) were quantified and are shown as means ± SD (n = 3), respectively. Maximal values of CCl4-treated rats without heat treatment are set at 100%. (E) Rats were heated at 42°C for 40 minutes and allowed to recover at room temperature for 6 hours (filled circle) or not heat treated (open circle). Then, CCl4 was injected intraperitoneally. At indicated times after CCI4 (1.0 mL/kg injection, serum ALT activity was measured, and the results are shown as means ± SE (n = 3). ALT, alanine aminotransferase