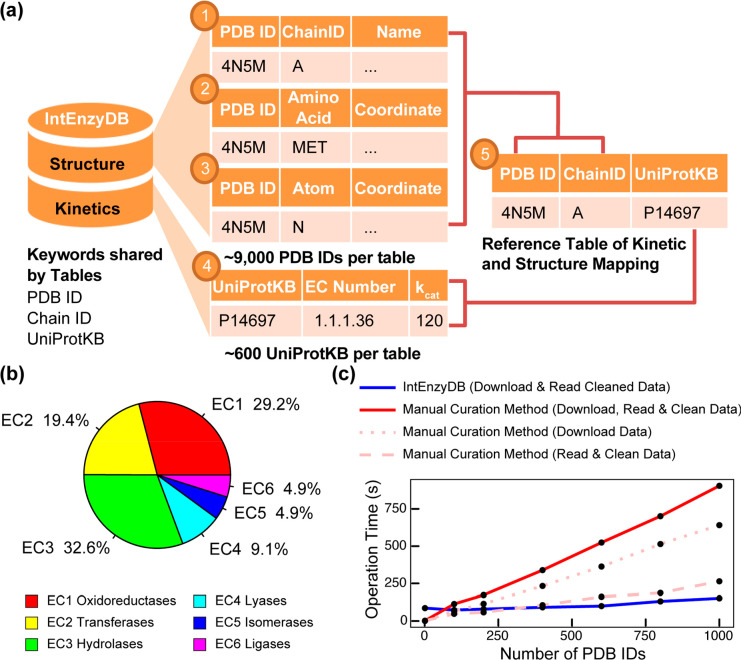
Figure 1.
Architecture, kinetics data statistics, and performance benchmark for IntEnzyDB. (a) The database architecture consists of five tables, including three tables for enzyme structure information (chain-level, amino acid-level, and atom-level), one table for kinetics, and a reference table that includes foreign keys from the structure and kinetics tables. The mapping of the tables is established using the PDB ID, Chain ID, and UniProtKB keys. (b) The distribution of kinetics data for six enzyme commission classes. (c) The comparison of operation time between IntEnzyDB and manual curation methods. The operation time for downloading, reading, and cleaning data is measured for processing 1, 100, 200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 PDB IDs, with data downloading and reading/cleaning indicated by dotted and dashed lines, respectively. The total operation time for the manual curation method is shown by the red solid line. All operation times are reported in seconds. Adapted with permission from ref (53). Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society.