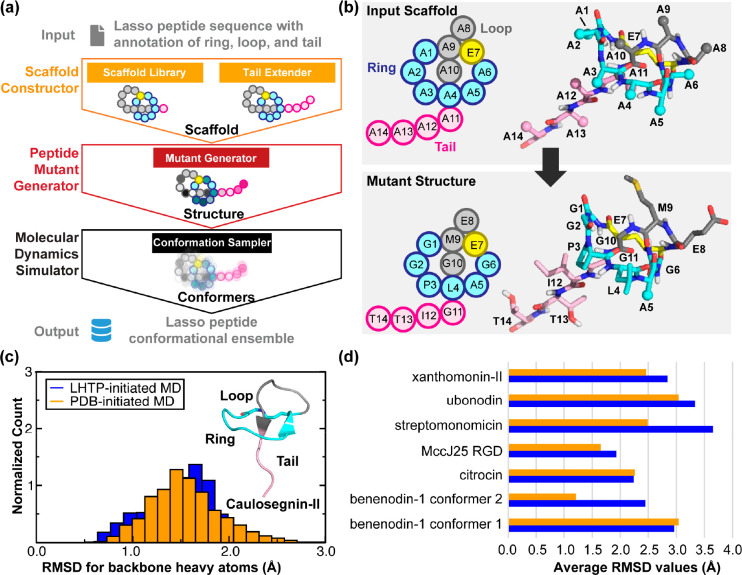
Figure 3.
Design framework and application of LassoHTP. (a) A schematic of LassoHTP’s workflow, which involves three modules: scaffold constructor, peptide mutant generator, and MD simulator, to transform a user-input sequence into a conformational ensemble. (b) Application of the mutant generator module to convert the poly alanine lasso peptide scaffold into the lasso peptide that is consistent with the user-input sequence. Sequence shown is for xanthomonin-II105 (PDB ID: 2MFV). (c) Distribution of root-mean-square deviation (RMSD) for LassoHTP-initiated and PDB-initiated MD conformational ensemble for caulosegnin-II.98 (d) Average RMSD values of LassoHTP (LHTP)-initiated (colored in blue) and PDB-initiated (colored in orange) MD ensembles for eight lasso peptides involved in the benchmark. The structures of the lasso peptides were determined mostly by NMR except for caulosegnin-II by X-ray crystallography (PDB ID: 5D9E). For (c) and (d), the RMSD was calculated using backbone atoms (i.e., Cα, N, C, and O) with reference to the reference crystal and NMR structure. Adapted with permission from ref (57). Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society.