Fig. 2 |. Validation of COVID-19-associated circuit chromatin sites and genes.
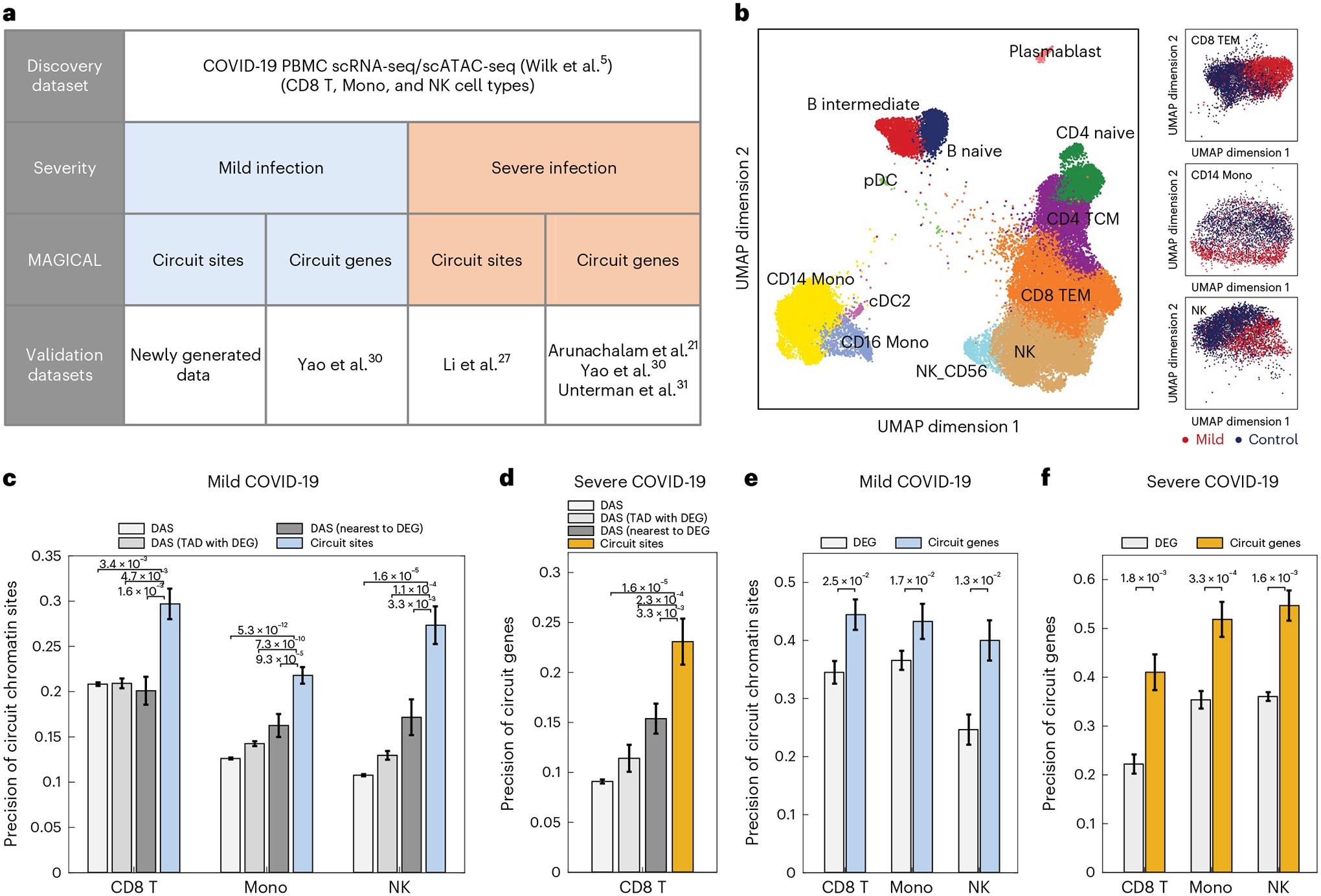
a, We applied MAGICAL to a COVID-19 PBMC single-cell multiomics dataset and identified circuits for the clinical mild and severe groups. We validated the MAGICAL-selected circuit sites and genes using newly generated and independent COVID-19 single-cell datasets. b, UMAPs of a newly generated independent scATAC-seq dataset including 16,000 cells from six people with COVID-19 and 9,000 cells from three controls showed chromatin accessibility changes in CD8 TEM, CD14 Mono, and NK cell types. c,d, The precision of MAGICAL-selected circuit sites is significantly higher than that of the original DAS, the nearest DAS to DEG, or all DAS in the same TAD with DEG. e,f, The precision of circuit genes are significantly higher than that of DEG. c,e, For mild COVID-19, MAGICAL identified 645 sites in CD8 TEM, 599 sites in CD14 Mono, and 148 sites in NK, regulating 153 genes, 183 genes, and 60 genes, respectively. d,f, For severe COVID-19, MAGICAL identified 78 sites, 202 sites, and 62 sites in the three cell types, regulating 25 genes, 81 genes, and 26 genes, respectively. c–f, Precision is defined as the proportion of the selected sites and genes to be differentially accessible and differentially expressed in the same cell type between infection and control conditions in independent datasets. Results are presented as bar plots where the heights represent the precision and the error bars represent the 95% confidence interval. Significance is evaluated using a two-sided Fisher’s exact test and P values between bars are shown.
