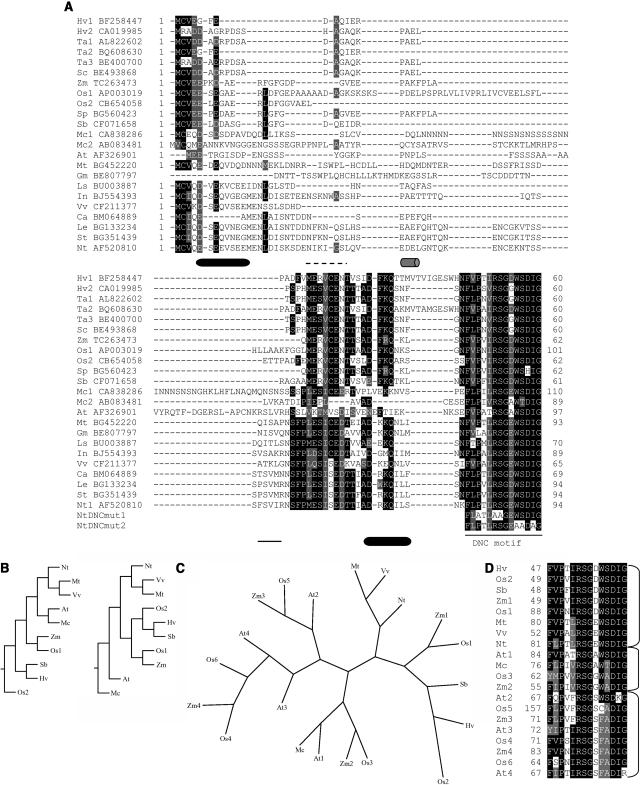
Figure 1.
A, Multiple sequence alignment of the N-terminal regions of the identified DBP-like factors. The alignment was generated with T-coffee (http://igs-server.cnrs-mrs.fr/Tcoffee/; Notredame et al., 2000) and viewed with Boxshade (http://www.ch.embnet.org/software/BOX_form.html). Black boxes denote sequence identity, whereas gray boxes refer to conservative changes. Dashes indicate gaps included for a better alignment. Species abbreviations: Hv, Hordeum vulgare; Ta, Triticum aestivum; Sc, Secale cereale; Zm, maize; Os, rice; Sp, Sorghum propinquum; Sb, Sorghum bicolor; Mc, Mesembryanthemum crystallinum; At, Arabidopsis; Mt, Medicago truncatula; Gm, Glycine max; Ls, Lactuca sativa; In, Ipomoea nil; Vv, Vitis vinifera; Ca, Capsicum annuum; Le, Lycopersicon esculentum; St, Solanum tuberosum; and Nt, tobacco. The GenBank accession number of each sequence is given. The consensus secondary structure prediction for the DBP1 N-terminal region provided by the Network Protein Sequence @nalysis server (NPS@; http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr) using default parameters (Combet et al., 2000) is indicated below the amino acid sequence; α-helices and β-strands are shown as cylinders and lines, respectively. Gray cylinder and dashed line denote uncertain prediction. The amino acid sequence of the DNC motif in the mutated DBP1 proteins is included at the bottom of the alignment. B, Phylogenetic trees generated using Phylip programs (http://bioweb.pasteur.fr/seqanal/phylogeny/phylip-uk.html). Full-length amino acid sequences were aligned using T-coffee (http://igs-server.cnrs-mrs.fr/Tcoffee/; Notredame et al., 2000). Left, Phylogenetic tree provided by Quicktree, a program for the rapid reconstruction of phylogenies by the Neighbor-Joining method (Howe et al., 2002). Right, Phylogenetic tree obtained with Fitch, a program that uses the Fitch-Margoliash and some related least-squares criteria. C, Unrooted phylogenetic tree generated with Quicktree (Howe et al., 2002), including full-length sequences containing less conserved DNC motifs. D, Multiple sequence alignment of the DNC motifs of the DBP-related sequences used in C.