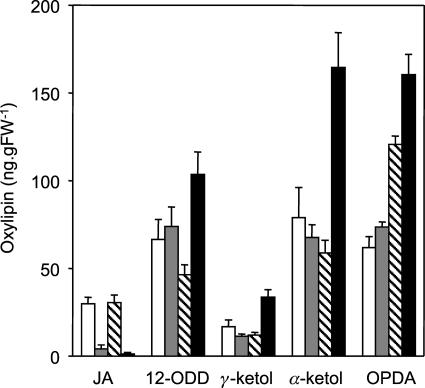
Figure 2.
cts mutants are JA deficient. Measurement of JA and oxylipin intermediates in cts mutants and respective wild types is shown. White bars, Wild-type Ler; gray bars, cts1; hatched bars, wild-type Ws; black bars, cts2. Values are means ± se from eight independent samples, each of which was analyzed in duplicate. Surface-sterilized seeds of the mutants cts1 and cts2 were plated on Gamborg's B5 salts, 0.7% (w/v) agarose, pH 5.8, for 4 d at 22°C in continuous light (150 μmol m−2 s−1) to confirm the phenotype. They were then transferred to plates, as above, supplemented with 0.5% (w/v) Suc and nicked to allow germination. Both mutants and wild-type seeds were stratified on the same media in the dark for 2 d at 4°C followed by germination for 7 d at 22°C. Seedlings were then transferred to soil in cellular trays and grown for 13 d under a long-day cycle (22°C, 16 h light/18°C, 8 h dark) at 150 to 170 μmol m−2 s−1, 60% relative humidity. For each mutant and wild type, there were 8 trays of 20 seedlings; from each tray, two replicate samples of rosette leaf were harvested, weighed, and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Oxylipins were quantified from 200 mg of tissue that was ground to powder and extracted overnight in 70:30 (v/v) acetone:50 mm citric acid with 20 ng prostaglandin A1 (Sigma, St. Louis) added as an internal standard. Oxylipins were extracted from the aqueous phase by partitioning 3 times with diethyl ether, evaporating to dryness, and resuspending in 60% methanol prior to HPLC tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Separation was achieved using a LUNA C18(2) 150 × 2-mm column (Phenomenex, Torrance, CA) and a methanol-water-0.2% formic acid gradient. Eluted compounds were fragmented by targeted tandem mass spectrometry using an LCQ mass spectrometer (Thermo Separation Products, Riviera Beach, FL), and the daughter ions identified and quantified using response factors calibrated between prostaglandin A1 and authentic oxylipin standards (Larodan, Malmo, Sweden).