Fig 8.
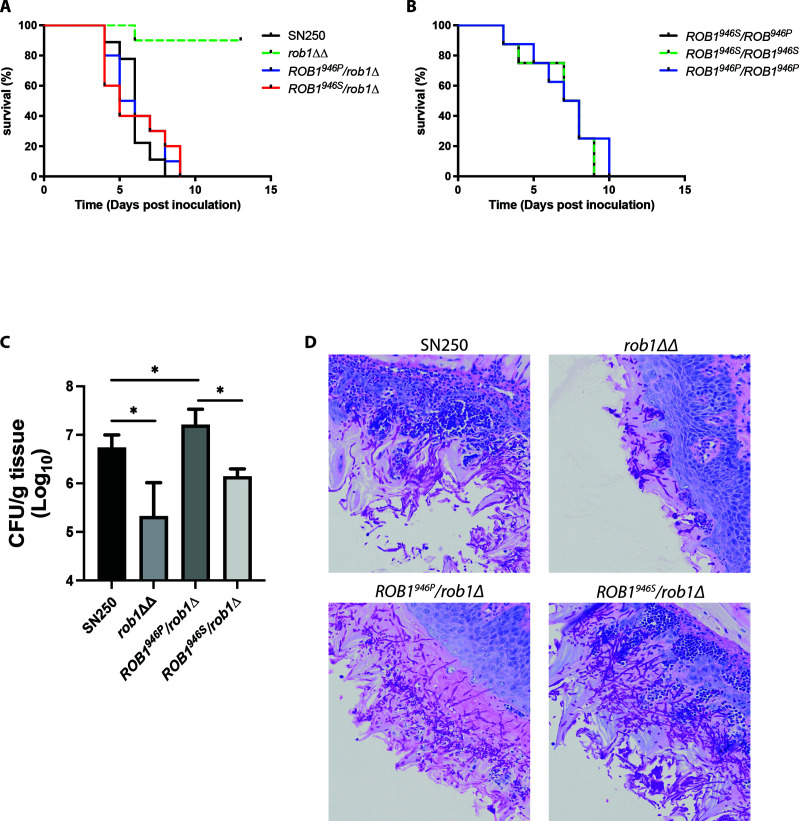
The ROB1946P allele promotes oral colonization while the ROB1946S allele promotes invasive infection. (A and B) Survival curves for CD-1 mice (n = 10/strain) infected with the indicated strains by tail-vein infection and monitored to moribundity. The rob1∆∆ mutant (A) was the only strain for which a statistically significant survival time was observed (Kaplan Meier, Mantel log-rank, P <0.05). (C) The oral fungal burden of tongues harvested from cortisone-treated CD-1 mice (5/strain) infected with the indicated strains 5 days post-infection. The bars are mean with standard deviation indicated by the error bars. The asterisks indicate statistically significant differences between strains denoted by the horizontal lines as determined by ANOVA with Dunnett’s test of multiple comparisons. (D) Histological analysis of tongues from infections described for panel C. The fields are representative of multiple fields evaluated.