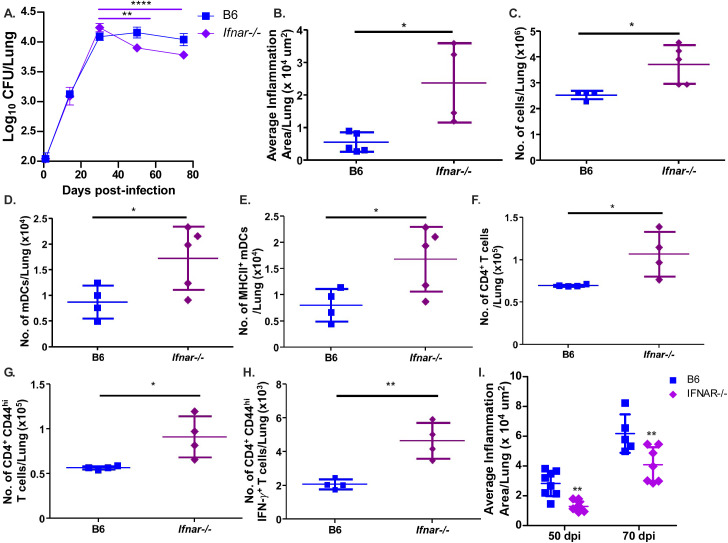
Fig 5.
rpoB-H445Y Mtb infection suppresses lung immune responses through a type I IFN-dependent pathway. B6 and Ifnar −/− mice were aerosol infected with a low dose of rpoB-H445Y Mtb. Mice were sacrificed for subsequent analyses at the indicated time points. Bacterial burden in (A) lung was determined. (B) FFPE lung sections were stained with H&E, and lung inflammatory area was measured at 30 dpi. (C) Total numbers of lung immune cells in single cell suspensions were determined at 30 dpi. (D) Total numbers of (E) MHC Class II+ mDCs, as well as the numbers of (F) total, (G) CD44+, and IFN+ (H) CD4+ T cells, were determined by flow cytometry at 30 dpi. (I) FFPE lung sections were stained with H&E, and lung inflammatory area was measured at 50 and 70 dpi. The data shown represent the means ± SD of four to five biological replicates per experiment. Significant differences are indicated with asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; P < 0.0001) by Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons tests (A–H) or by two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test (I). One of two independent experiments is shown.