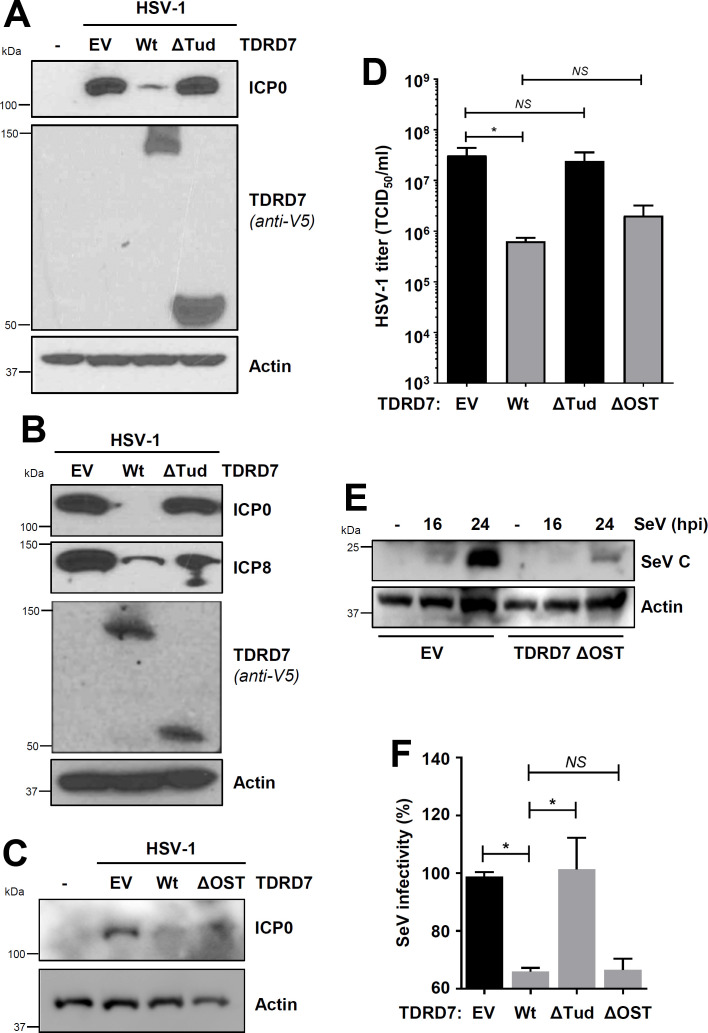
Fig 5.
AMPK interaction is required for the antiviral activity of TDRD7 against HSV-1 and SeV. (A) HEK293T cells, transfected with Wt or ΔTud mutant of TDRD7, were infected with HSV-1 (multiplicity of infection [MOI], 1), and viral protein (ICP0) expression was analyzed 24 hpi by immunoblot. (B) TDRD7 KO HT1080 cells, stably expressing Wt or ΔTud mutant of TDRD7, were infected with HSV-1 (MOI, 1), and viral proteins (ICP0 and ICP8) were analyzed 24 hpi by immunoblot. (C) TDRD7 KO cells, stably expressing EV, Wt, or ΔOST mutant of TDRD7, were infected with HSV-1, and viral protein (ICP0) expression was analyzed by immunoblot. (D) TDRD7 KO cells, stably expressing Wt, ΔTud, or ΔOST mutants of TDRD7, were infected with HSV-1 (MOI, 1), and infectious viral particles were analyzed 24 hpi by TCID50/mL. (E) HEK293T cells, stably expressing ΔOST mutant of TDRD7, were infected with SeV, and viral protein (SeV C) expression was analyzed by immunoblot. (F) HEK293T cells, transfected with Wt, ΔTud, or ΔOST mutants of TDRD7, were infected with SeV, and viral replication was quantified by flow cytometric analyses of viral antigen expression 16 hpi. The SeV antigen expression of EV was considered 100, and all other values were normalized to this. The results are representative of three experiments; the data represent mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05; EV, empty vector; NS, nonsignificant.