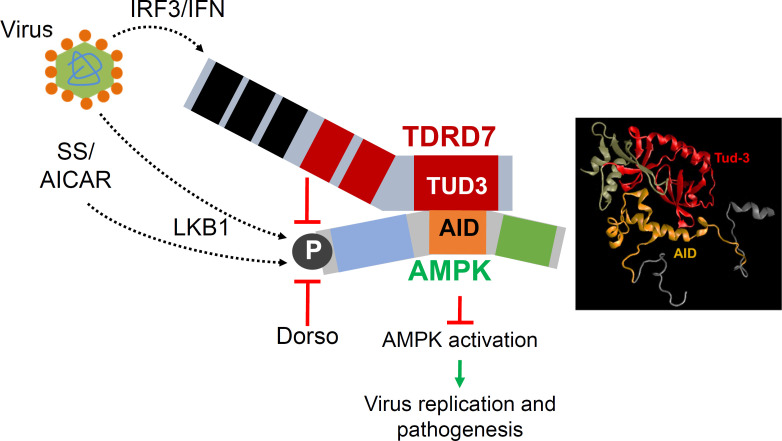
Fig 8.
A model representing IFN-inducible protein TDRD7 interacts with pro-viral AMPK and inhibits its activation to suppress viral replication and pathogenesis. Virus infection, via IRF3/IFN pathway, transcriptionally induces TDRD7, which interacts with AMPK via the C-terminal Tudor domain, to inhibit AMPK activation. Various inducers, e.g., virus infection, serum starvation (SS), or AICAR, activate LKB1, the kinase that directly phosphorylates AMPK. Inhibition of AMPK activation by TDRD7 is a molecular basis for its viral restriction activity. The TDRD7-AMPK branch is a novel antiviral pathway of the IFN system.