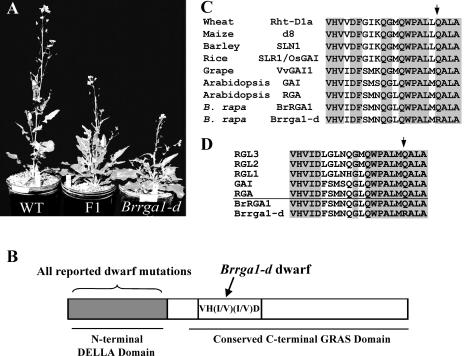
Figure 1.
Mutation of the conserved Q residue in the VHIID region of BrRGA1 causes dwarfism. A, Phenotypes of near-isogenic B. rapa plants: homozygous wild-type BrRGA1 (WT), heterozygous BrRGA1/Brrga1-d (F1), and homozygous Brrga1-d. B, Structure of DELLA proteins showing positions of mutations causing dwarfism. Mutations in the N terminus result in dwarf plants in wheat (Rht-B1b, Rht-D1b), maize (D8-Mp1, D8-1, D8-2023), Arabidopsis (gai, rga-Δ17, rgl1-Δ17), barley (Sln1d), rice (slrΔDELLA), and grape (Vvgai1; Peng et al., 1999; Dill et al., 2001; Boss and Thomas, 2002; Chandler et al., 2002; Itoh et al., 2002; Wen and Chang, 2002), while Brrga1-d dwarf B. rapa is caused by a mutation in the C-terminal region. C and D, Amino acid sequence alignment comparing VHIID regions of Brrga1-d and BrRGA1 with those of other DELLA proteins functioning as GA signaling repressors from different plant species (C) or with all five Arabidopsis DELLA proteins that control diverse processes of plant growth and development (D). Arrows indicate position of the mutated amino acid in Brrga1-d.