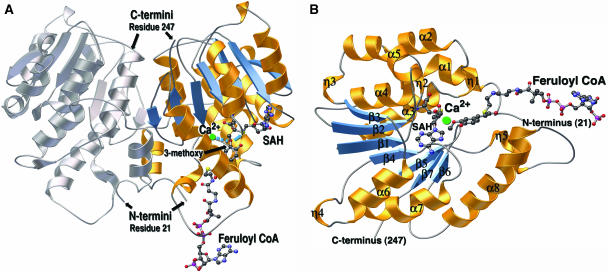
Figure 3.
Ribbon diagrams of the CCoAOMT three-dimensional structure. A, Ribbon diagram of the alfalfa CCoAOMT homodimer, with one monomer colored (helices are gold and β-strands are blue) and the other monomer in gray. The dyad axis is oriented vertically in the plane of the page. The SAH and feruloyl CoA molecules are depicted as colored ball and sticks (carbon is black; nitrogen is blue; oxygen is red; and sulfur is yellow). The Ca2+ ion is in green. A coordination bond from the Ca2+ ion to the 3-methoxy oxygen of feruloyl CoA is shown as a dashed blue line. A blue arrow points from the same oxygen to the sulfur position on SAH that is attached to the reactive methyl group in SAM. The N-terminal and C-terminal amino acid residues visible in the final electron density map are numbered. B, Ribbon diagram of the CCoAOMT monomer. The SAH and feruloyl CoA molecules are depicted as ball and sticks and color-coded as in A. Secondary structures are numbered according to Figure 2. α is α-helix, β is β-strand, and η is 3/10 helix. Ribbon diagrams were produced with MOLSCRIPT (Kraulis, 1991) and rendered with POV-RAY (http://www.povray.org).