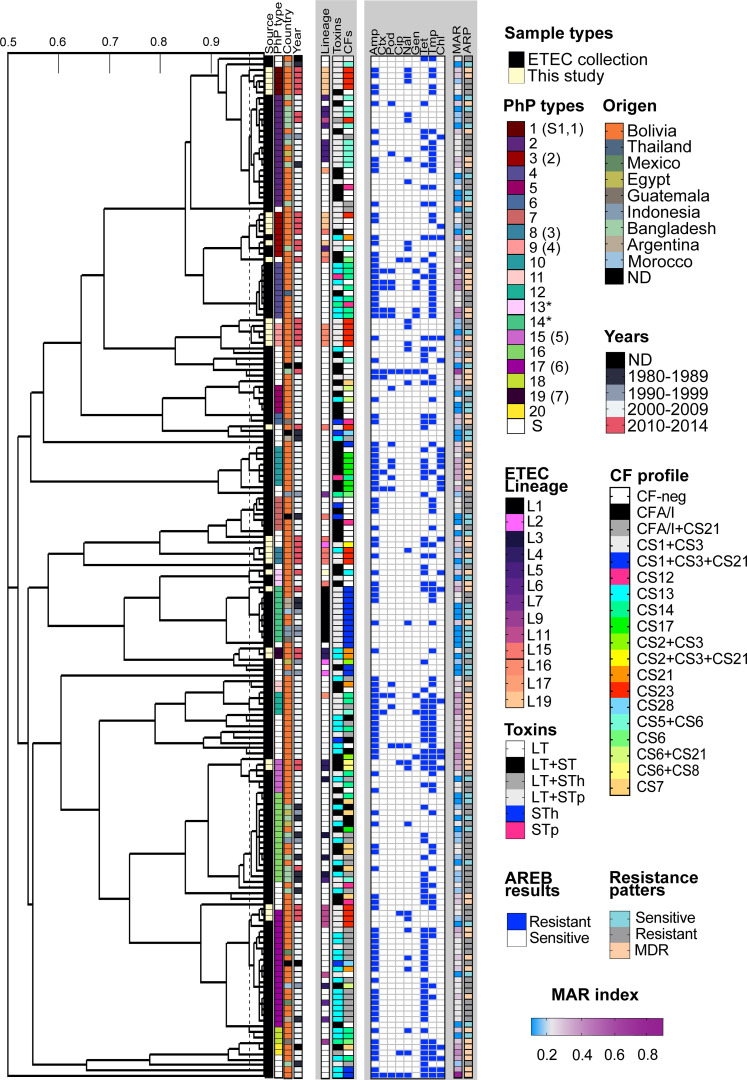
Fig 5.
Comparison of phenotypic fingerprints from a collection of clinical Bolivian ETEC strains and isolates obtained in this study. The dendrogram shows the clustered PhP typing data, including the antibiotic resistance patterns obtained parallel by the AREB system. Information about the place and year of isolation, ETEC lineage, toxin, and CF profile are indicated in the legends in the figure. ETEC lineage information was included only for isolates from von Mentzer’s ETEC collection. Isolates from this study yielded different PhP numbers and the former PhP assignment from Fig. 4 is shown in parentheses. Antibiotic resistance to the nine AREB antibiotics, the multiple antibiotic resistance index (MAR), and antibiotic resistance patterns such as sensitivity, resistance, and multidrug resistance (MDR, ≤3 classes of antibiotics) were incorporated into the heatmap. The white coloration in the MAR index gradient indicates the critical limit of the MAR of 2. AMP, ampicillin; CTX, cefotaxime; POD, cefpodoxime; CIP, ciprofloxacin; NAL, nalidixic acid; GEN, gentamycin; TET, tetracycline; and CHL, chloramphenicol.