FIGURE 4.
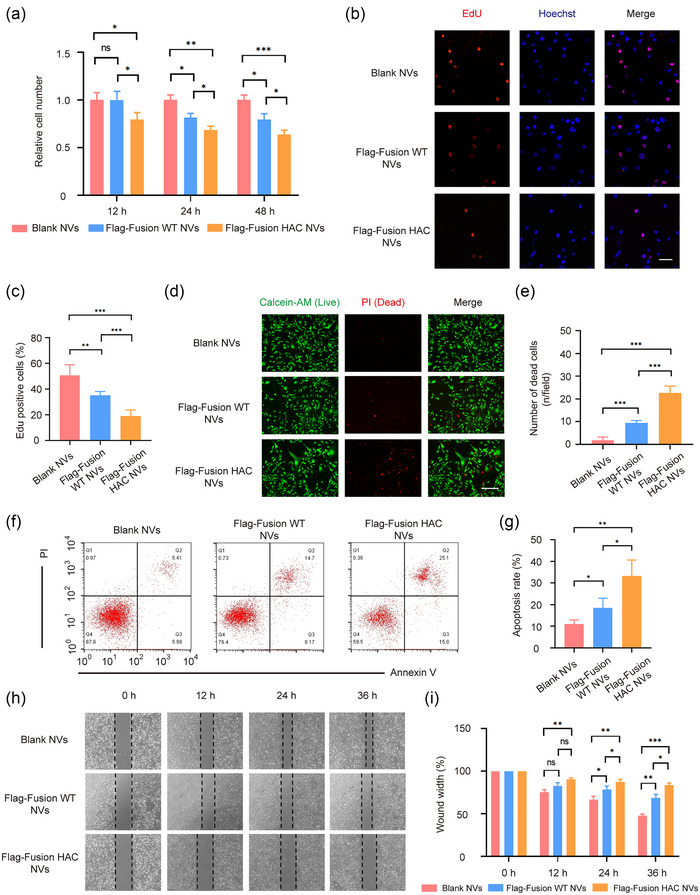
HAC NVs inhibit immune‐independent tumour cell growth and migration. (a) Cell viability for 12, 24 and 48 h after MDA‐MB‐231 cells were treated with 100 μg Blank, Flag‐Fusion WT and Flag‐Fusion HAC NVs, respectively (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001). (b) Fluorescence images of dividing MDA‐MB‐231 cells in each group (Red: Edu staining; Blue: Hoechst staining). Scale bar: 50 nm. (c) Quantification of proportion of dividing cells in (b) (n = 5, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). (d) Fluorescence images of survival and death of MDA‐MB‐231 cells in each group (Green: Calcein‐AM staining; Red: PI staining). Scale bar: 100 nm. (e) Quantification of proportion of dead cells in (d) (n = 3, ***p < 0.001). (f) Representative images of apoptotic status of MDA‐MB‐231 cells treated with 100 μg Blank, Flag‐Fusion WT or Flag‐Fusion HAC NVs for 48 h. (g) Quantitative analysis of cell apoptosis in (f) (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01). (h) Wound healing assay of MDA‐MB‐231 cells treated with different NVs. Representative images of cell migration were shown. (i) Quantitative analysis of wound closure in (h) (n = 3, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001).
