Figure 4.
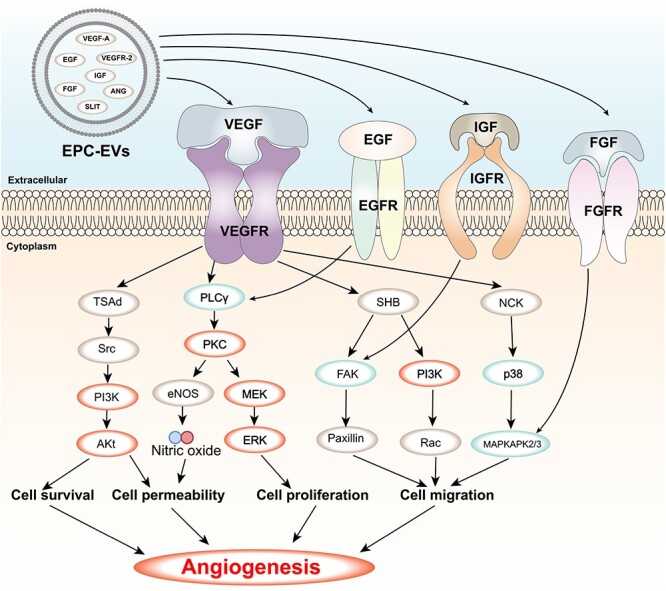
VEGF signalling pathway and its regulation by EVs contents. VEGF is a key factor that stimulates the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones or from the embryonic circulatory system. VEGF binds to its receptors (VEGFRs) on the surface of endothelial cells and activates various downstream pathways, such as Ras/MAPK, FAK/paxillin, PI3K/AKT and PLCγ/PKC, that regulate cell proliferation, migration, survival, permeability and angiogenesis. EVs are small membrane vesicles that are released by various cell types and contain bioactive molecules, such as proteins and RNAs. EVs can modulate the VEGF signalling pathway by delivering their contents to target cells or by interacting with VEGFRs on the cell surface. Some of the EVs contents that have been shown to affect the VEGF signalling pathway are SLIT, IGF, ANG, EGF, FGF, VEGFR-2 and VEGF-A. The figure shows the main components and effects of the VEGF signalling pathway and how EVs regulate this pathway through their contents. FGF Fibroblast growth factor, FGFR FGF receptor, IGF insulin-like growth factor, IGFR IGF receptor, EGF epidermal growth factor, EGFR EGF receptor, MAPKAPK2/3 mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2/3, MEK MAPK/ERK kinase, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, Ra, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate, PI3K phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38 p38 MAPK, NCK non-catalytic region of tyrosine kinase adaptor protein, FAK focal adhesion kinase, SHB Src homology 2 domain-containing adapter protein B, eNOS endothelial nitric oxide synthase, PKC protein kinase C, PLCγ phospholipase C gamma, AKT protein kinase B, Src proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src, TSAd T cell-specific adapter protein, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGFR VEGF receptor, EVs extracellular vesicles
