Figure 5.
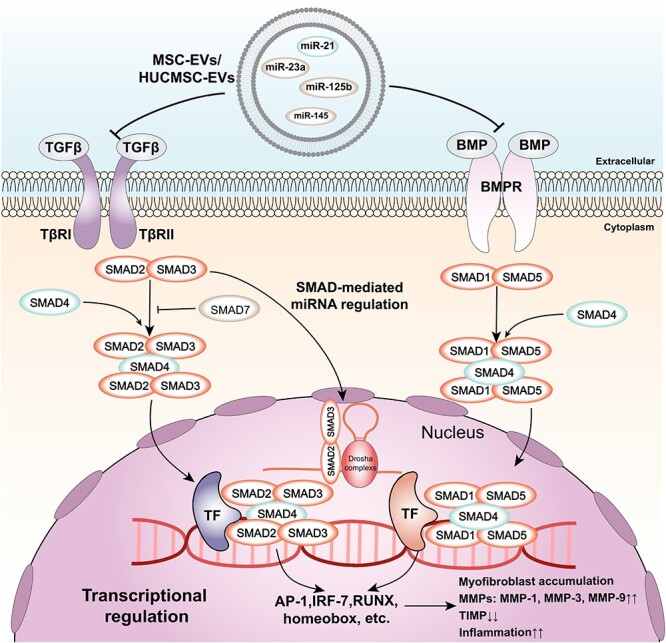
TGF-β signalling pathway and its regulation by EVs. The figure shows the major components and regulatory effects of TGF-β signalling and how cellular EVs regulate TGF-β signalling through inclusions. TGF-β and BMP bind to their respective receptors (TβRII and BMPR) and activate SMAD proteins (SMAD2/3 for TGFβ and SMAD1/5 for BMP). SMAD4 forms complexes with SMAD2/3 or SMAD1/5 and translocates to the nucleus, where it interacts with transcription factors (TF) to regulate gene expression. SMAD-mediated miRNA regulation involves Drosha complexes and SMAD2/3. The final effect of TGFβ signalling is myofibroblast accumulation, MMPs and TIMP expression, and an inflammatory condition. Exosome contents, such as miR-145, miR-125b, miR-23a and miR-21, can modulate TGFβ signalling by targeting different components of the pathway. TβRII TGF-β receptor type II, TGF-β transforming growth factor beta, BMPR bone morphogenetic protein receptor, BMP bone morphogenetic protein, TF transcription factor, AP-1 activator protein 1, IRF-7 interferon regulatory factor 7, RUNX runt-related transcription factor, MMPs matrix metalloproteinases, TIMP tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases, miR microRNA, EVs extracellular vesicles
