Figure 6.
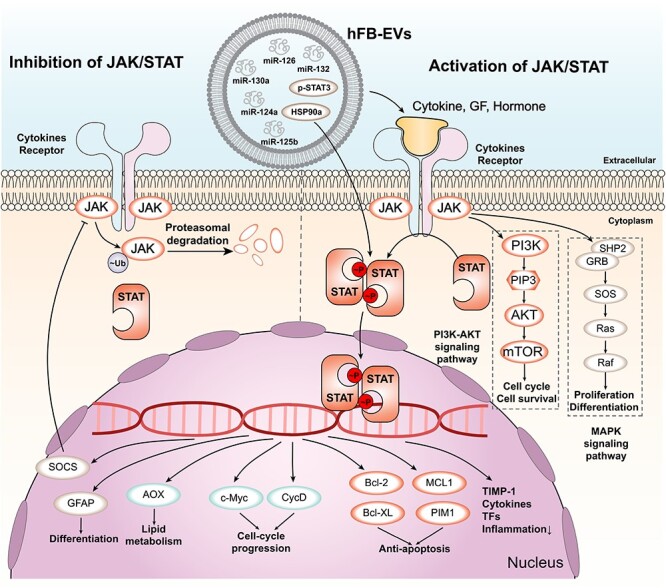
JAK/STAT signalling pathway and its regulation by EVs. The main components of the JAK/STAT signalling pathway are shown. Cytokines, growth factors (GF) and hormones bind to their receptors on the cell membrane, activating JAK kinases that phosphorylate (p) STAT proteins. p-STAT proteins form dimers and translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate the transcription of target genes. Ubiquitylated JAK proteins are degraded by proteasomes. The downstream target genes of p-STAT proteins include those involved in anti-apoptosis, cell-cycle progression, lipid metabolism and differentiation. Some examples of these genes are PIM1, MCL1, Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, CycD, c-Myc, AOX, GFAP, SOCS, TIMP-1, cytokines and transcription factors (TFs). The JAK/STAT signalling pathway interacts with other signalling pathways, such as the PI3K-AKT and MAPK pathways. The PI3K-AKT pathway regulates cell cycle and survival through AKT, PIP3, PI3K and mTOR. The MAPK pathway regulates proliferation and differentiation through Raf, Ras, SOS, SHP2, GRB2 and ERK. EVs are extracellular vesicles that contain various molecules, such as microRNAs (miRNAs), proteins and lipids. EVs can modulate the JAK/STAT signalling pathway by delivering or removing some of these molecules. For example, EVs can carry miR-124a, miR-130a, miR-125b, HSP90a, p-STAT3, miR-132 and miR-126 to target cells and affect their gene expression and signalling activity. EVs extracellular vesicles, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TIMP-1 tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases, MAPK mitogen-activated protein kinase, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase
