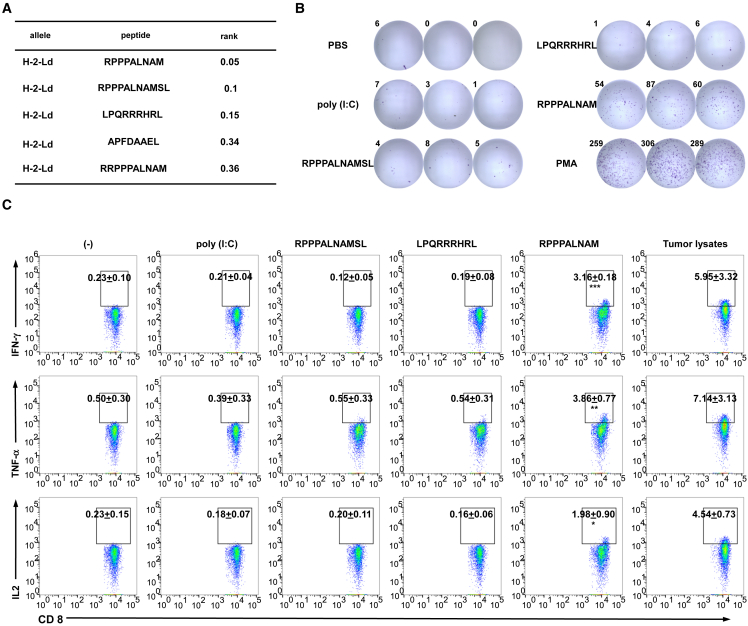
Figure 2.
uPeptides of RNF10 are immunogenic
(A) The binding predictions for RNF10 uPeptides to H2-d MHC class I using the Immune Epitope Database (version 2.5) analysis resource NetMHCpan (ver. 4.1) algorithm. (B) Splenocytes of vaccinated mice were restimulated with the RNF10 uPeptide antigens used for vaccination. The specificity of splenocytes to the RNF10 uPeptide was assess by IFN-γ ELISpot. Representative ELISpot images are shown; spot count per 5 × 105 cells is presented. (C) Splenocytes of mice injected with CT26 cells and vaccinated with peptides and the polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (poly[I:C]) adjuvant (CT26, n = 3) were tested for recognition of mutated peptides by flow cytometry. Intracellular cytokine staining of CD8+ T cells, evaluated by flow cytometry. Percentages of cytokine-producing T cells are shown (mean ± SD, n = 3). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 compared with untreated T cells (−). p-values were determined by two-tailed one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple-comparisons test.