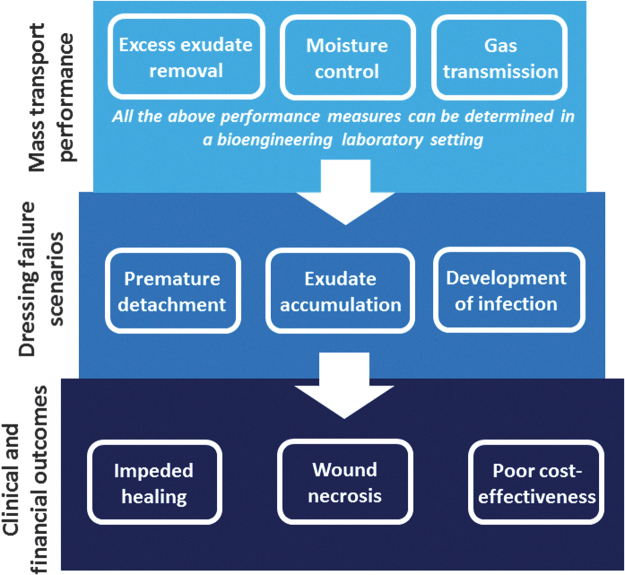
Figure 2.
The fluid handling (or mass transport) performance of a certain wound dressing (as detailed in Table 1), which can be measured in a bioengineering laboratory setting, determines the likelihood of that dressing to successfully manage exudates, or alternatively, to fail in the more challenging clinical scenarios requiring, for example, the absorbency of high volume of exudation or of a viscous exudate; treatment of infected wounds; and protection of fragile periwound skin. Hence, the mass transport performance of the dressing eventually determines both the patient and the financial outcomes.