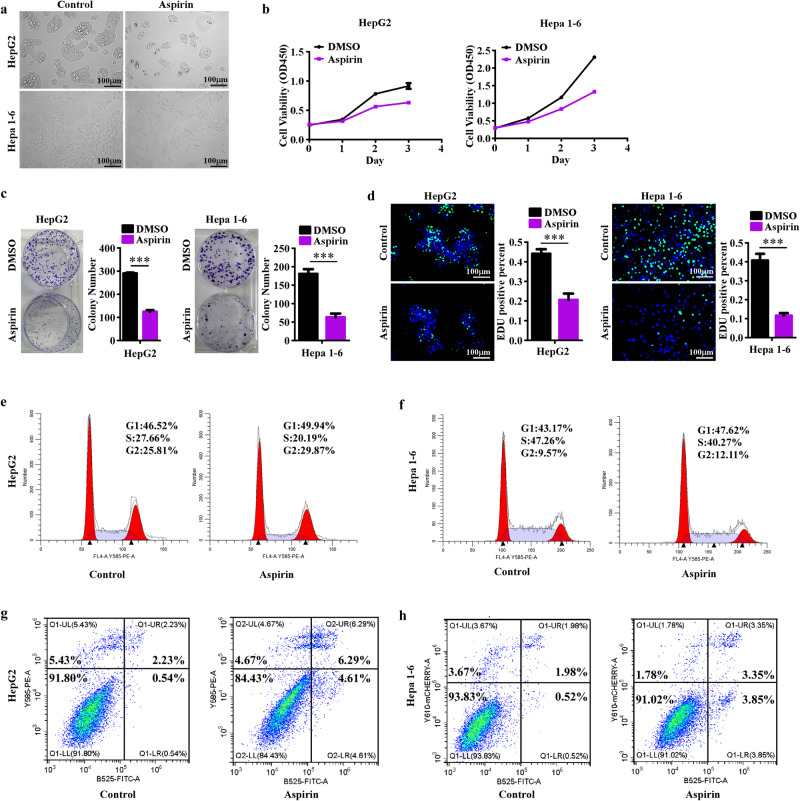
Fig. 1. Aspirin inhibits the growth of HCC cells.
a Representative images of HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells treated with 4 mM aspirin and control solution for 48 h. b CCK8 assays reveal cell growth curves of HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells treated with 4 mM aspirin and control solution. c Representative images (left) and relative quantification (right) for the colony formation assays of HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells with different treatments. d Representative micrographs (left) and relative quantification (right) for the EdU assays of HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells with different treatments. e, f Cell cycle detection assays display the growth inhibition of aspirin on HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells. g, h Cell apoptosis detection assays show the apoptosis induction of aspirin on HepG2 and Hepa1-6 cells. Error bars represent the means of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.